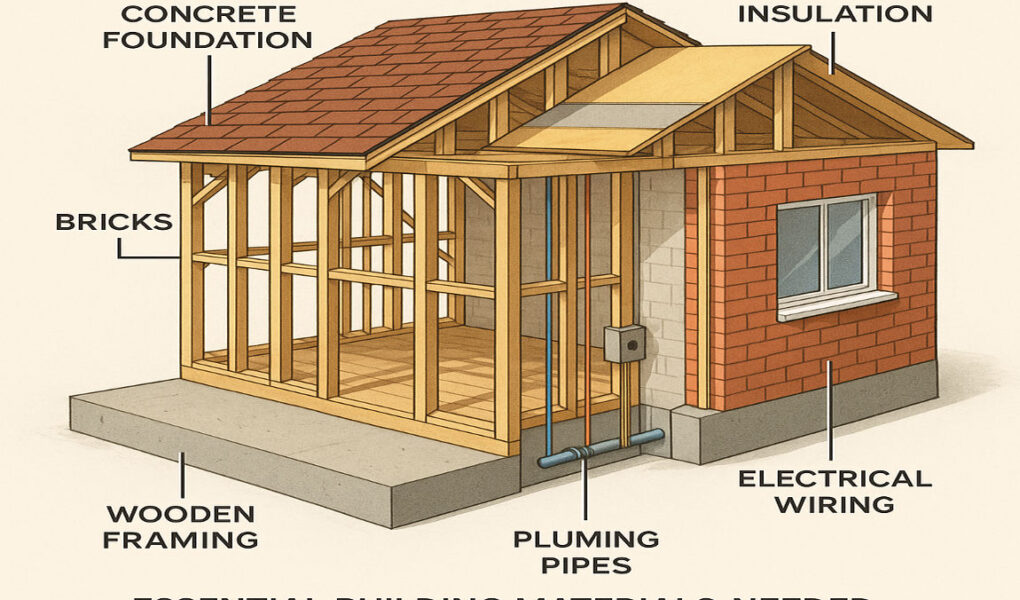
Building a house is one of the most significant investments you’ll ever make. Whether you’re constructing your dream home or a practical living space, the materials you choose play a crucial role in determining the durability, safety, and aesthetics of your house. Selecting the right materials needed to build a home is not just about cost—it’s about creating a structure that stands the test of time, adapts to your climate, and reflects your style.
What Are Building Materials?
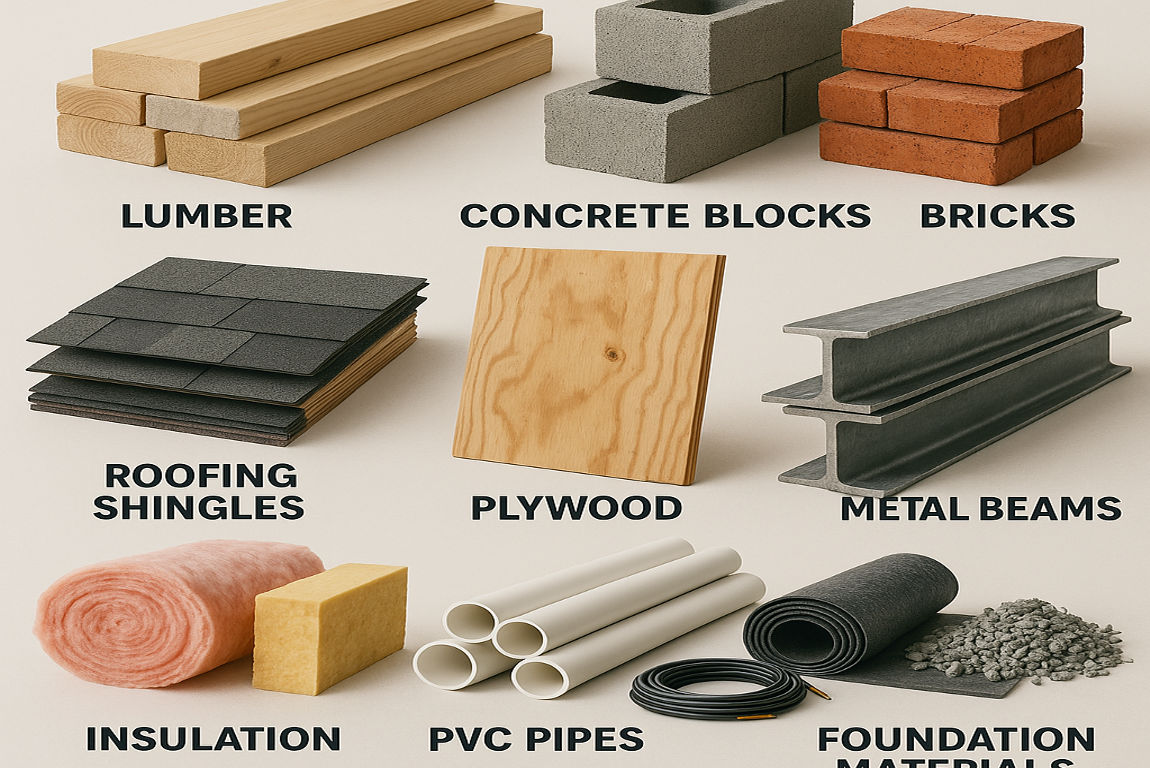

Before diving into the specifics, let’s start with the basics: What are building materials?
Building materials are the substances used in the construction of structures, including homes, offices, and other buildings. These materials can be natural, like wood and stone, or manufactured, like concrete and steel. The choice of materials directly impacts the quality, durability, and appearance of your home.
Why Are Building Materials Important?
The materials you choose affect:
- Structural Integrity: Strong materials ensure your house can withstand environmental forces, such as wind, rain, and earthquakes.
- Energy Efficiency: Proper insulation and the use of sustainable materials can significantly reduce energy consumption.
- Aesthetics: Materials like wood, stone, or glass contribute to the overall look and feel of your home.
- Cost: Some construction materials are more affordable but may require frequent maintenance, while others are expensive upfront but last longer.
Categories of Building Materials
Building materials can be broadly categorized into:
- Natural Materials: Wood, stone, clay, etc.
- Manufactured Materials: Concrete, steel, bricks, etc.
Essential Materials Needed to Build a House: From Foundation to Roof
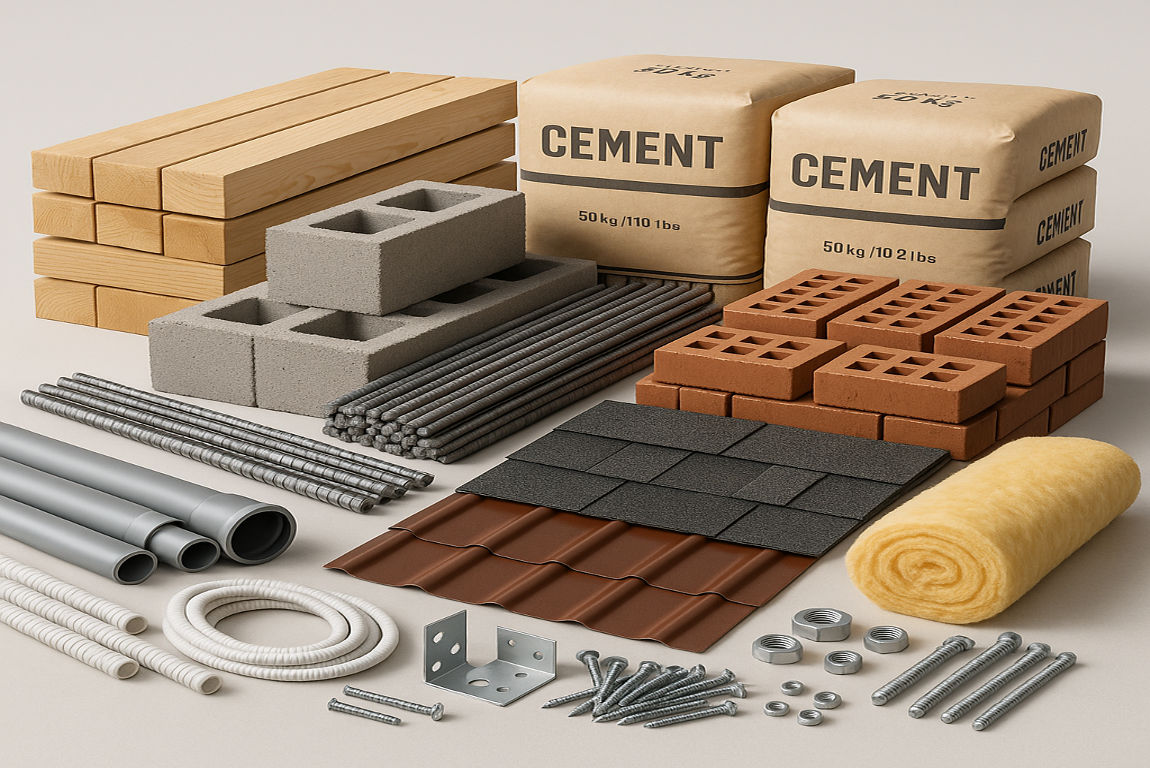

Building a house involves several stages, each requiring specific materials. Let’s break it down step by step.
Foundation Materials
The foundation is the backbone of your house. It supports the entire structure and ensures stability.
Concrete
Concrete is the most commonly used material for foundations. It’s a mixture of cement, water, sand, and aggregates. Its strength and durability make it ideal for supporting heavy loads.
- Pros: Strong, durable, fire-resistant.
- Cons: Can crack over time if not properly reinforced.
Steel Reinforcement Bars (Rebar)
Rebar is used to reinforce concrete, providing tensile strength and preventing cracks from forming.
- Pros: Increases the strength of concrete.
- Cons: Susceptible to corrosion if not treated properly.
Aggregates and Sand
These materials are mixed with cement to create concrete. Aggregates provide bulk, while sand ensures a smooth finish.
Quick Tip: Choose foundation materials based on your soil type and climate. For example, clay-heavy soil may require deeper foundations.
Structural Frame Materials
The structural frame forms the skeleton of your house, supporting walls, floors, and the roof.
Wood/Lumber
Wood is a popular choice for framing due to its versatility and natural insulation properties.
- Pros: Renewable, easy to work with, aesthetically pleasing.
- Cons: Prone to termites and moisture damage.
Steel
Steel is a modern alternative to wood, offering superior strength and durability.
- Pros: Fire-resistant, long-lasting, recyclable.
- Cons: Expensive, requires skilled labor for installation.
Comparison Table: Wood vs. Steel Framing
FeatureWoodSteel
Cost Affordable Expensive
Durability Prone to pests/moisture Highly durable
Sustainability Renewable Recyclable
Installation is Easy. Requires skilled labor
Wall Construction Materials
Walls define the layout of your construction home, providing insulation and protection.
Bricks
Bricks are a classic choice for wall construction, known for their durability and fire resistance.
- Pros: Long-lasting, low maintenance, sound thermal insulation.
- Cons: Heavy, labor-intensive to install.
Concrete Blocks
Concrete blocks are larger than bricks and are often used for modern construction.
- Pros: Cost-effective, strong, quick to install.
- Cons: Less aesthetic appeal compared to bricks.
Stone
Stone offers a natural and timeless look.
- Pros: Extremely durable, weather-resistant.
- Cons: Expensive, heavy, and labor-intensive.
Eco-Friendly Alternatives
- Adobe: Made from clay and straw, ideal for dry climates.
- Hempcrete: Lightweight and sustainable.
- Cob: A mixture of clay, sand, and straw, offering excellent insulation.
Roofing Materials
The roof protects your home from the elements and contributes to its overall design.
Tiles (Clay, Concrete)
Tiles are a durable and attractive roofing option.
- Pros: Long lifespan, weather-resistant.
- Cons: Heavy, expensive.
Metal Roofing
Metal roofs are lightweight and modern.
- Pros: Durable, recyclable, low maintenance.
- Cons: Noisy during rain, can dent easily.
Asphalt Shingles
A popular and affordable choice for residential roofs.
- Pros: Cost-effective, easy to install.
- Cons: Shorter lifespan compared to tiles or metal.
Insulation Materials
Insulation is essential for maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature and reducing energy costs.
Types of Insulation:
- Fiberglass: Affordable and widely used.
- Foam: Excellent for house sealing gaps and cracks.
- Cellulose, made from recycled paper, is an eco-friendly material.
Tip: Choose insulation based on your climate. For colder regions, thicker insulation is recommended.
Finishing Materials
Finishing house materials add the final touches to your home, enhancing its beauty and functionality.
Glass
Used for windows, doors, and skylights, glass allows natural light to flood your home.
Wood
Ideal for flooring, doors, and trims, wood adds warmth and elegance.
Tiles and Stone
Perfect for flooring and decorative finishes, tiles and stone are durable and stylish.
Paints and Coatings
Paints protect surfaces and add color to your home. Opt for weather-resistant coatings for exterior walls.
Plumbing and Electrical Materials
Plumbing
Pipes, fittings, and fixtures are essential for water supply and drainage.
Electrical
Wiring, switches, and outlets ensure a safe and functional electrical system.
How to Choose the Right Materials Needed to Build a House
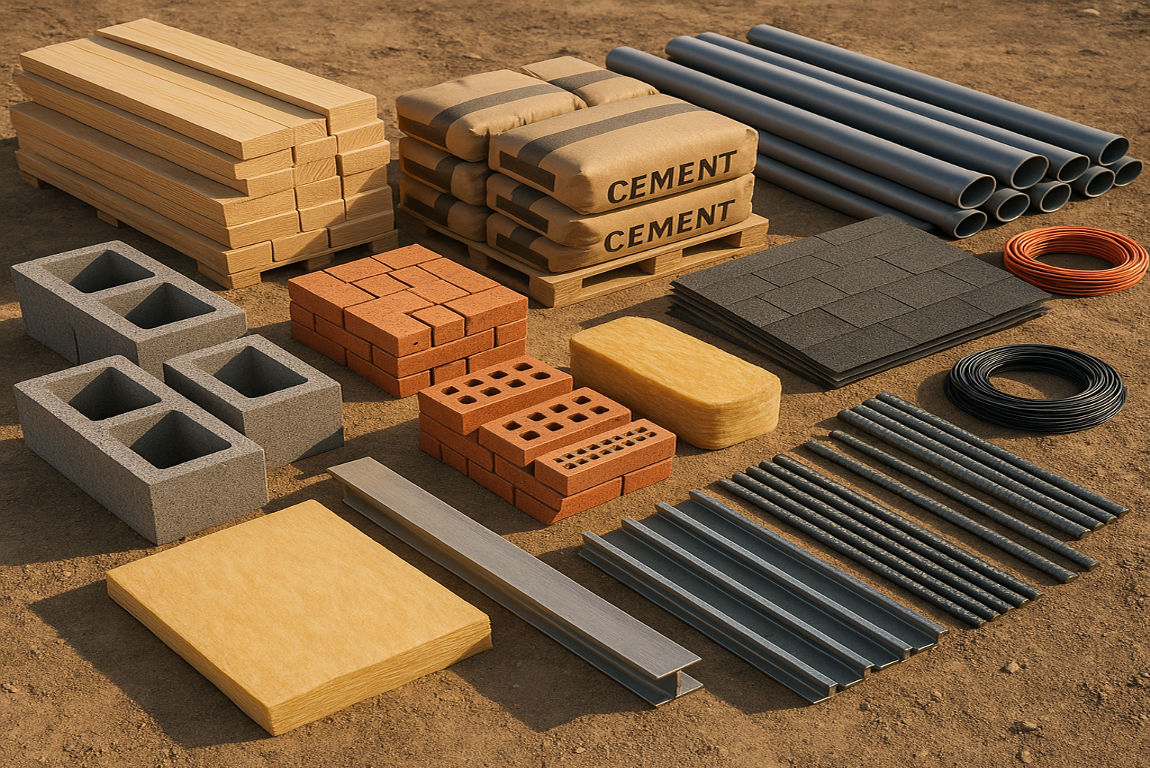

Selecting the right construction materials can be overwhelming. Here are some tips to help you make informed decisions:
- Consider Your Budget: Strike a Balance Between Cost and Quality.
- Consider Climate: Select materials that are well-suited to your local weather conditions.
- Prioritize Sustainability: Opt for eco-friendly materials whenever possible.
- Consult professionals, such as architects and contractors, who can provide valuable advice.
Emerging Trends in House Building Materials
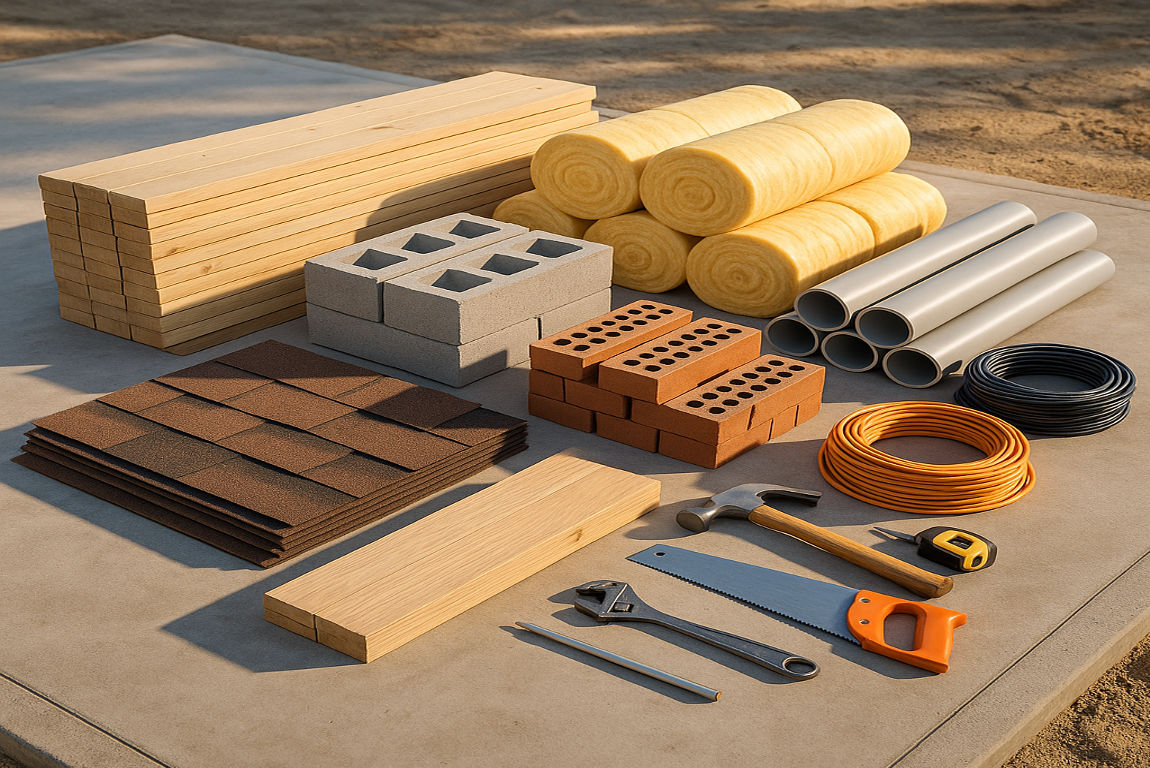

The construction industry is evolving, with new materials and technologies emerging.
Sustainable Materials
- Recycled Steel: Reduces waste and energy consumption.
- Bamboo: A fast-growing, renewable resource.
- Hempcrete: Lightweight and carbon-negative.
Smart Materials
- Self-healing concrete.
- Energy-efficient glass.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Choosing the cheapest house materials over quality.
- Ignoring climate suitability.
- Overlooking maintenance requirements.
- Not verifying material certifications.
Materials Needed to Build a House FAQ
What are the basic materials needed to build a house?
The basic materials needed to build a house include:
- Foundation materials: Concrete, rebar, and gravel
- Framing materials: Lumber, nails, and screws
- Exterior materials: Bricks, siding, or stucco
- Roofing materials: Shingles, tiles, or metal sheets
- Insulation materials: Fiberglass, cellulose, or spray foam
- Interior finishing materials: Drywall, paint, and flooring
- Plumbing and electrical materials: Pipes, wires, and fixtures
What type of foundation materials are commonly used?
The most common foundation materials used in residential construction are:
- Concrete: Used for poured concrete foundations and footings
- Rebar: Steel reinforcement bars used to strengthen concrete
- Gravel: Used as a base layer for the foundation to provide drainage and stability
What are the best framing materials for a house?
The most common framing materials for a house are:
- Lumber: Dimensional lumber, such as 2x4s and 2x6s, is the most widely used framing material
- Engineered wood: Laminated veneer lumber (LVL) and oriented strand board (OSB) are also popular choices for framing
- Steel: Steel framing is becoming more popular due to its durability and resistance to pests and fire
What are the most common exterior materials for a house?
The most common exterior materials for a house are:
- Brick: Durable and low-maintenance, brick is a popular choice for its classic look
- Siding: Vinyl, fiber cement, and wood siding are all popular options for their affordability and versatility
- Stucco: A durable and low-maintenance option that can be applied to a variety of surfaces
What are the best roofing materials for a house?
The most common roofing materials for a house are:
- Asphalt shingles: Affordable and easy to install, asphalt shingles are the most popular roofing material
- Clay or concrete tiles: Durable and long-lasting, tile roofs are a popular choice in warmer climates
- Metal roofing: Durable, long-lasting, and eco-friendly, metal roofs are gaining popularity
What are the most effective insulation materials for a house?
The most effective insulation materials for a house are:
- Fiberglass: The most common insulation material, fiberglass is affordable and easy to install
- Cellulose: Made from recycled paper, cellulose insulation is eco-friendly and effective
- Spray foam: A more expensive option, spray foam insulation provides excellent thermal performance and air sealing
What are the best interior finishing materials for a house?
The best interior finishing materials for a house depend on your personal style and budget, but some popular options include:
- Drywall: The most common wall finish, drywall is affordable and easy to install
- Paint: A wide range of colors and finishes are available to suit your style
- Flooring: Hardwood, tile, and carpet are all popular flooring options
What plumbing and electrical materials are needed for a house?
The plumbing and electrical materials needed for a house include:
- Pipes: Copper, PEX, and PVC pipes are all commonly used for plumbing
- Wires: Copper and aluminum wires are used for electrical wiring
- Fixtures: Sinks, toilets, faucets, and light fixtures are all essential components of a house