When planning to build a 2000 sq ft house, one of the most essential steps is estimating the number of bricks required. Accurately calculating brick requirements is critical for budgeting, ensuring timely delivery of materials, and avoiding unnecessary delays or wastage during construction.
Understanding the Basics of Brick Calculation
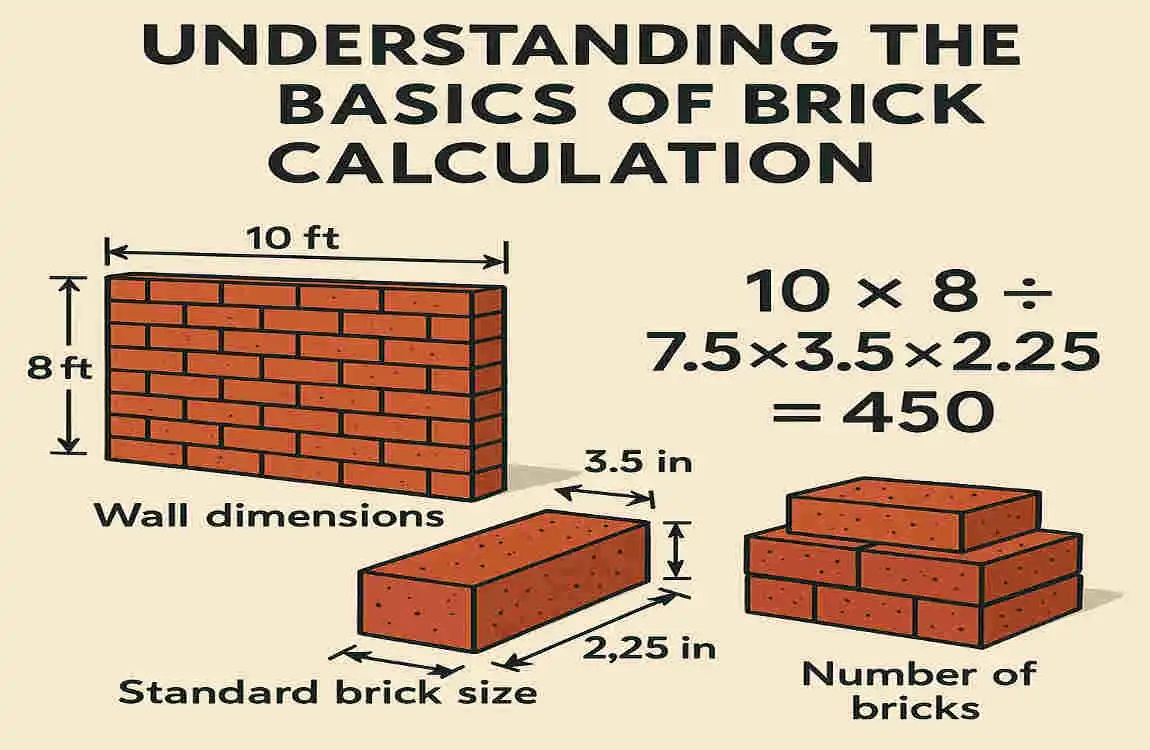
Before jumping into calculations, it’s essential to understand the factors that influence the number of bricks required. These include the wall area, brick size, and mortar thickness.
What Determines Brick Quantity?
The number of bricks required depends on the following primary factors:
- Wall Area: The total wall surface area, in square feet, is the starting point for any calculation.
- Brick Size: Different types of bricks have varying dimensions, which directly impact the quantity needed.
- Mortar Thickness: Mortar joints between bricks typically reduce the number of bricks required per square foot.
Standard Brick Sizes and Types
Here are some of the commonly used brick sizes:
- Standard Brick (Inches): 7.5″ x 3.5″ x 2.25″
- Modular Brick (Inches): 7.8″ x 3.8″ x 2.25″
- Nominal Brick Sizes: These include the mortar thickness and differ slightly by region or country.
Brick Type Length (in)Width (in)Height (in)
Standard Brick 7.5 3.5 2.25
Modular Brick 7.8 3.8 2.25
The Role of Mortar Joints
Mortar joints (usually 0.5 inches thick) fill the gaps between bricks, slightly reducing the number of bricks needed per square foot. Accounting for mortar thickness is crucial for accurate calculations.
How to Calculate the Number of Bricks for a House
Let’s take a closer look at the step-by-step process for calculating the number of bricks required for a construction house.
Step-by-Step Method
- Calculate Wall Area:
- Measure the house’s perimeter and multiply it by the wall height to get the total wall surface area.
- For instance, in a 2000 sq ft house with a perimeter of 200 feet and a wall height of 10 feet, the wall area would be:
- 200 ft (perimeter) x 10 ft (height) = 2000 sq ft
- Subtract Openings:
- Deduct the area of doors and windows from the total wall area. For example, if the total area of doors and windows is 200 sq ft, the effective wall area becomes:
- 2000 sq ft – 200 sq ft = 1800 sq ft
- Calculate Bricks per Square Foot:
- For standard bricks with mortar joints, approximately seven bricks are required per square foot of wall area.
- Multiply Wall Area by Bricks per Square Foot:
- Multiply the effective wall area by the number of bricks per square foot to estimate the total number of bricks.
- 1800 sq ft x 7 bricks/sq ft = 12,600 bricks
Average Brick Requirement for a 2000 Sq Ft House
The exact number of bricks can vary based on several factors, but here’s a general estimate:
Single-Story vs. Two-Story Houses
- Single-story house: Typically requires around 12,000 to 15,000 bricks.
- Two-story house: Requires approximately 20,000 to 25,000 bricks, as the wall area doubles.
Wall Thickness and Design
- Single Brick Wall: Walls built with one brick thickness (4 inches) require fewer bricks.
- Double Brick Wall: Walls with double brick thickness (9 inches) require significantly more bricks.
- Cavity Walls: These use more bricks due to the additional layers and structural design.
Factors Influencing Brick Requirements
Architectural Complexity
Curved walls, intricate home designs, and decorative patterns often require more bricks than standard straight walls.
Brick Type
The size and material of bricks (e.g., clay bricks, concrete bricks) significantly influence the count. Larger bricks cover more area, reducing the total number required.
Wastage and Breakage
Always account for a 5-10% wastage allowance to cover breakage, cutting, and other unforeseen losses.
Quick Estimate of Bricks for a 2000 Sq Ft House
If you’re looking for a quick approximation, here’s a breakdown of brick requirements based on different construction types:
Construction Type Approx. Bricks Needed
Single-story house 12,000 – 15,000
Two-story house 20,000 – 25,000
Cavity walls 25,000+
Tips for Quick Estimation
- Use online calculators for a rough estimate. Websites like BrickCalculator.com offer reliable tools.
- When in doubt, consult with your contractor or architect for precise calculations.
Practical Example: Brick Calculation for a 2000 Sq Ft House

Let’s walk through a realistic calculation to solidify your understanding.
Assumptions:
- Perimeter: 200 feet
- Wall Height: 10 feet
- Door and Window Openings: 200 sq ft
- Brick Size: Standard (7.5″ x 3.5″ x 2.25″)
Calculation:
- Total Wall Area:
- 200 ft x 10 ft = 2000 sq ft
- Effective Wall Area:
- 2000 sq ft – 200 sq ft = 1800 sq ft
- Bricks per Square Foot:
- 7 bricks
- Total Bricks Needed:
- 1800 sq ft x 7 bricks/sq ft = 12,600 bricks
Budgeting Based on Brick Estimates
How Brick Quantity Affects Costs
The number of bricks directly affects construction costs. Here’s what you should keep in mind:
- Brick Prices: Vary by type and location. For example, clay bricks might cost $0.50 per unit, while concrete bricks might cost $0.60.
- Transportation Costs: Factor in the delivery charges for transporting bricks to your site.
- Wastage Costs: Include an allowance for breakage and cutting.
Tips for Budgeting:
- Order slightly more than your estimate to avoid shortages.
- Compare prices from multiple suppliers to get the best deal.
Common Mistakes in Estimating Brick Requirements
Avoid these common errors in brick estimation:
- Ignoring Wastage: Failing to account for breakage often leads to shortages.
- Not Subtracting Openings: Overestimating due to unaccounted door and window areas.
- Misjudging Wall Thickness: Double walls and cavity walls require more bricks than single walls.
Alternatives to Bricks and Their Impact
Common Alternatives
- Concrete Blocks: Larger and faster to install, but more expensive.
- AAC Blocks (Autoclaved Aerated Concrete): Lightweight, thermally efficient, and require fewer units.
Impact on Material Calculation
Switching to alternatives like AAC blocks can reduce the overall count but may increase costs.