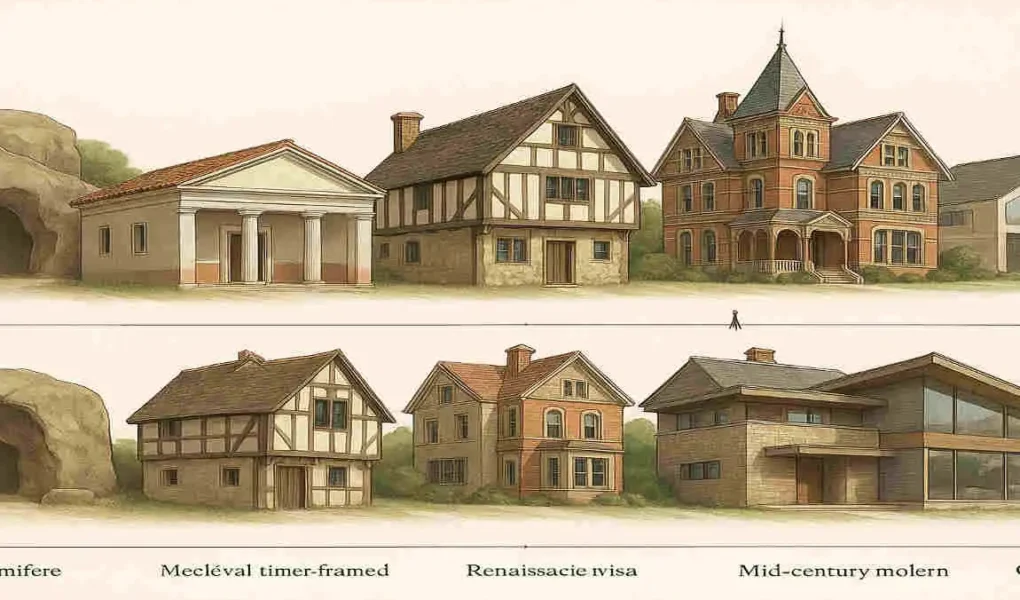
Have you ever wondered how the homes we live in today came to be? From ancient caves to modern smart homes, the evolution of house architecture is a fascinating journey that reflects the changing needs, technologies, and aspirations of humanity.
Understanding the history of house architecture is more than just an enjoyable trip down memory lane. It can help us appreciate the homes we live in today and inspire us to create better living spaces for the future.
Origins of Shelter: The Earliest Forms of Housing
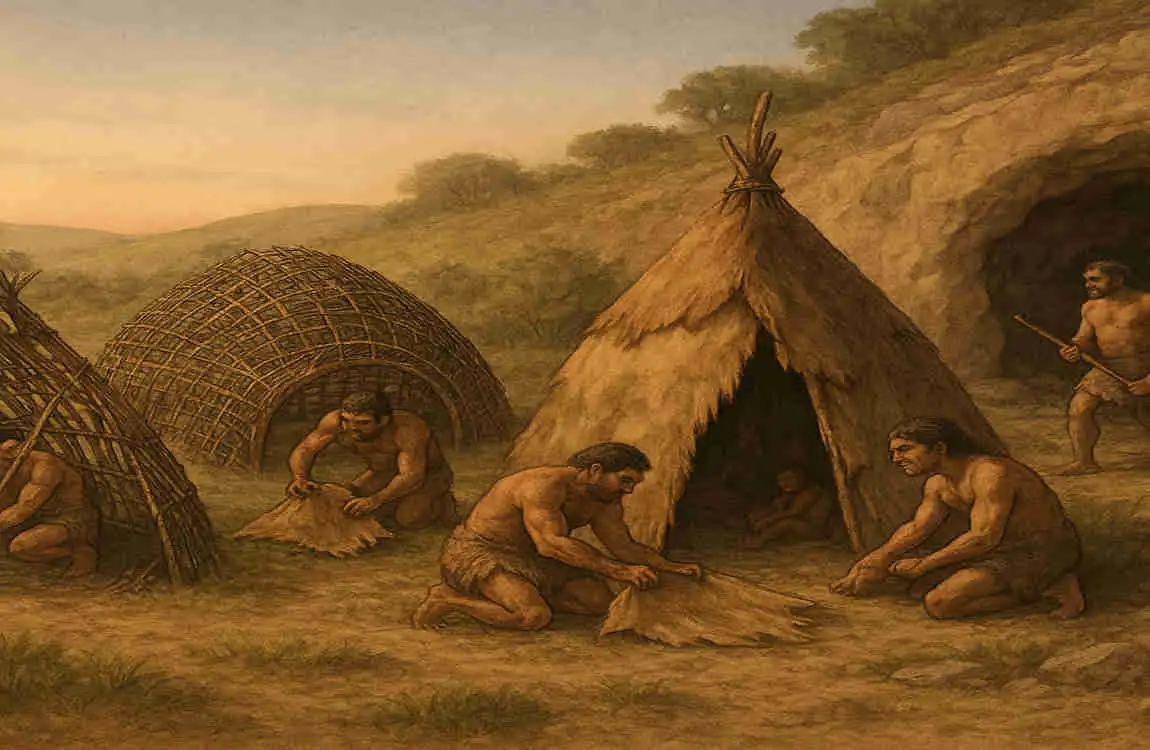

The First Human Shelters
Our story begins with the very first human shelters. In the earliest days of our species, people sought refuge in natural caves or constructed simple huts using whatever materials they could find in their environment. These primitive dwellings were all about survival – keeping out the elements, protecting against predators, and providing a safe space to rest and regroup.
Materials Used in Early Shelters
The materials used in these early shelters were dictated by what was readily available in the surrounding environment. Stone, wood, and animal hides were common choices, as they could be sourced directly from nature without the need for complex tools or technologies. These natural materials provided the necessary protection and insulation, even if they weren’t always the most comfortable or long-lasting.
Focus on Protection and Survival
In those early days, the primary concern was survival. Aesthetics and comfort were secondary to the need for a secure shelter that could withstand the elements and keep the inhabitants safe. The design of these early homes was driven by practicality and necessity, rather than any grand architectural vision.
Influence of Environment and Culture
The specific design of early shelters was heavily influenced by the local environment and the cultural practices of the people who built them. In colder climates, for example, people might have used animal hides to create insulated dwellings, while in warmer regions, lightweight thatched roofs might have been more common. As human societies developed and spread across the globe, these early architectural choices laid the foundation for the diverse styles we see today.
Ancient Civilizations and the Birth of Architectural Styles

Overview of Housing in Ancient Civilizations
As human societies grew more complex, so too did their architecture. In ancient civilizations like Mesopotamia, Egypt, Greece, and Rome, we see the emergence of more permanent and sophisticated housing styles. These early civilizations laid the groundwork for many of the architectural principles and techniques that we still use today.
Introduction of Permanent Materials
One of the key developments in ancient architecture was the use of more permanent materials. Mud bricks, stone, and early forms of concrete allowed for the construction of more durable and long-lasting structures. These materials not only provided better protection and insulation but also opened up new possibilities for architectural design and ornamentation.
Influence of Religion and Social Hierarchy
In many ancient societies, religion and social hierarchy played a significant role in shaping architectural styles. Temples and palaces were often the most impressive and ornate structures, reflecting the power and prestige of the ruling classes. Even in more modest homes, religious beliefs and social status could influence everything from the layout of the house to the decorative elements used.
Key Architectural Features
Several key architectural features emerged during this period that would go on to shape future styles. Courtyards, for example, became a common feature in many ancient homes, providing a private outdoor space for relaxation and social gatherings. Columns and arches were also widely used, both for their structural properties and their aesthetic appeal.
Setting the Foundation for Future Styles
The innovations and architectural principles developed by ancient civilizations laid a strong foundation for the styles that would follow. From the grand temples of Egypt to the elegant villas of Rome, these early designs showcased the potential of architecture to not only provide shelter but also to inspire and uplift the human spirit.
The Middle Ages: Defense and Social Status in Architecture
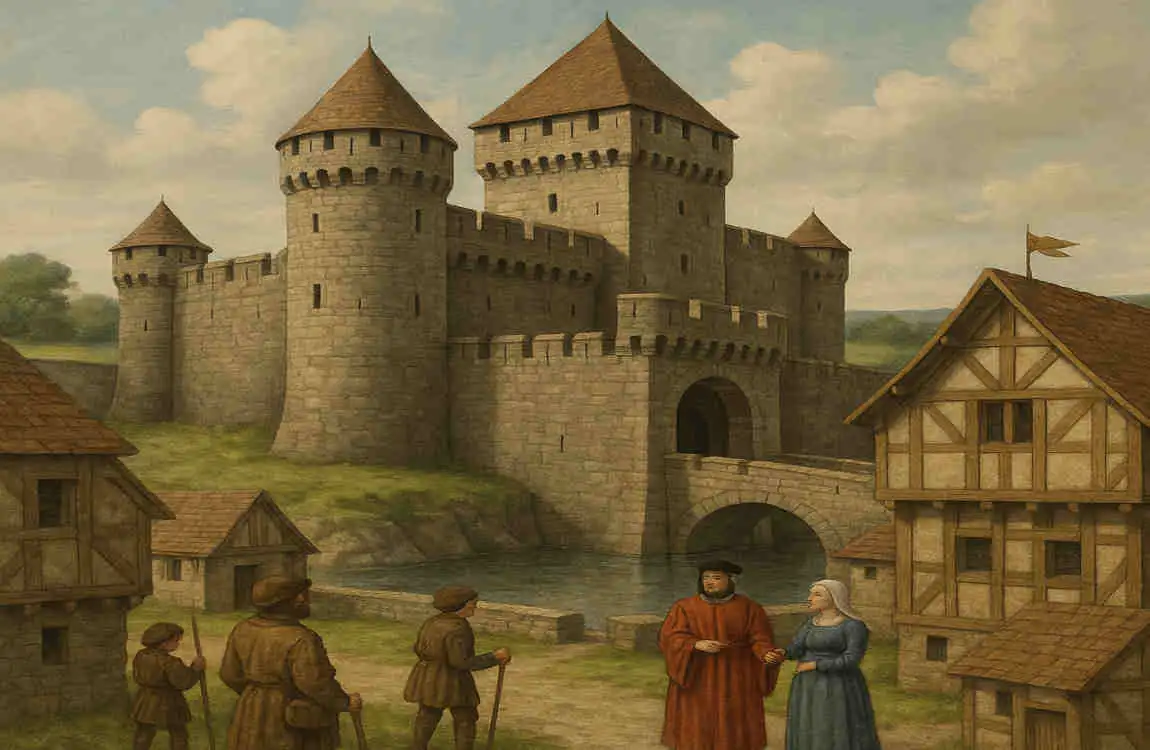

Transformation of Houses During the Middle Ages
The Middle Ages, spanning roughly from the 5th to the 15th century, brought significant changes to house architecture. As societies shifted and new threats emerged, homes evolved to meet the changing needs of their inhabitants.
Small Wooden Houses vs. Fortified Castles
During this period, we see a stark contrast between the simple wooden houses of the ordinary people and the grand, fortified castles and manors of the nobility. While the former were modest and functional, the latter were designed to be imposing and defensible, with thick walls, towers, and moats to protect against invaders.
Architectural Elements for Defense
Many of the architectural elements that emerged during the Middle Ages were driven by the need for defense. Thick walls, narrow windows, and strategically placed towers were all designed to make these structures more difficult to breach. Moats, drawbridges, and other defensive features further enhanced the security of these homes.
Emergence of Gothic and Tudor Styles
As the Middle Ages progressed, we see the emergence of new architectural styles like Gothic and Tudor. These styles were characterized by ornate decoration, pointed arches, and intricate stonework. In addition to their aesthetic appeal, these elements often carried symbolic meaning, reflecting the religious and cultural values of the time.
Houses as Status Symbols and Community Centers
In medieval society, a person’s home was not just a place to live but also a reflection of their social status and a center of community life. The grander the stunning house, the higher the status of its owner. Castles and manors often served as gathering places for the local community, hosting feasts, celebrations, and other social events.
Renaissance to Industrial Revolution: Harmony and Innovation

Renaissance Architecture: Revival of Classical Principles
The Renaissance, which began in the 14th century, marked a renewed interest in the classical principles of balance, proportion, and ornamentation. In-house architecture meant a return to the use of columns, domes, and symmetrical layouts, inspired by the grand buildings of ancient Greece and Rome.
Use of Columns, Domes, and Symmetry
Renaissance homes often featured grand entrances with columns, echoing the Style of ancient temples. Domes, both large and small, were used to create a sense of grandeur and harmony. Symmetrical layouts, with rooms arranged around a central axis, were also standard, reflecting the Renaissance ideal of order and balance.
Impact of the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, which began in the late 18th century, brought about profound changes in house architecture. The rise of urbanization and the development of new construction materials like iron, steel, and glass opened up new possibilities for design and construction.
Shifts to Mass Housing and Elaborate Victorian Homes
As cities grew and industrialization transformed the economy, there was a growing need for mass housing to accommodate the working classes. This led to the development of new housing types like tenements and row houses, designed to be affordable and efficient. At the same time, the wealthy embraced elaborate Victorian homes, characterized by ornate decoration, complex floor plans, and the latest technological innovations.
Rise of New Architectural Styles
The period from the Renaissance to the Industrial Revolution saw the rise of several new architectural styles. The Victorian Style, with its ornate decoration and eclectic mix of influences, was particularly popular among the wealthy. The Arts and Crafts movement, which emerged in the late 19th century, emphasized simplicity, craftsmanship, and a return to traditional materials and techniques. Art Nouveau, with its flowing lines and organic forms, also gained popularity during this time, influencing everything from furniture design to house architecture.
20th Century Modernism: Functionality and New Technologies

Shift from Ornamentation to Minimalism
The 20th century modern house brought about a significant shift in architectural thinking, with a move away from ornamentation and towards minimalism and functionality. This shift was driven in part by new technologies and materials, as well as changing social and economic conditions.
Early Modernism: International Style and Clean Lines
Early modernism, often referred to as the International Style, was characterized by clean lines, simple forms, and a focus on function over decoration. Steel, concrete, and glass were widely used, allowing for new structural possibilities and a more open, airy feel in homes.
Mid-Century Modernism: Open Floor Plans and Integration with Nature
Mid-century modernism, which emerged in the mid-20th century, built on the principles of early modernism while adding its own unique twists. Open floor plans, which allowed for more flexible and adaptable living spaces, became popular. There was also a renewed focus on integrating homes with their natural surroundings, with large windows and outdoor living areas becoming standard features.
Late Modernism and Postmodernism: Individuality and Playful Design
As the 20th century progressed, we saw the emergence of late modernism and postmodernism, which brought a renewed focus on individuality and playful design. While still rooted in the principles of modernism, these styles allowed for more eclectic and personal expressions of architecture, with a mix of old and new influences and a willingness to experiment with form and function.
Contemporary Architecture: Sustainable and Smart Homes

Emergence of Eco-Friendly Materials and Energy-Efficient Designs
In recent years, there has been a growing focus on sustainability and energy efficiency in house architecture. Eco-friendly materials like bamboo, recycled steel, and reclaimed wood are becoming more popular, as are designs that maximize natural light and ventilation. Green roofs, solar panels, and other sustainable features are also increasingly common in contemporary homes.
Smart Homes: Integration of Technology for Convenience and Security
Another major trend in contemporary architecture is the rise of smart homes, which integrate technology to enhance convenience, security, and sustainability. From automated lighting and climate control to innovative security systems and energy management, these homes are designed to make life easier and more efficient for their inhabitants.
Focus on Customization, Multi-Functionality, and Indoor/Outdoor Blending
Contemporary homes often prioritize customization and multi-functionality, with flexible spaces that can adapt to the changing needs of their inhabitants. There is also a growing trend towards blending indoor and outdoor spaces, with features like sliding glass walls and expansive decks that create a seamless transition between the two.
Examples of Popular Modern Styles
Some of the most popular modern styles include minimalism, with its focus on simplicity and clean lines; industrial, which draws inspiration from factories and warehouses; and eco-conscious, which prioritizes sustainability and environmental responsibility. Each of these styles reflects the values and priorities of contemporary society, showcasing the ongoing evolution of house architecture.
Factors Influencing Architectural Evolution Over Time
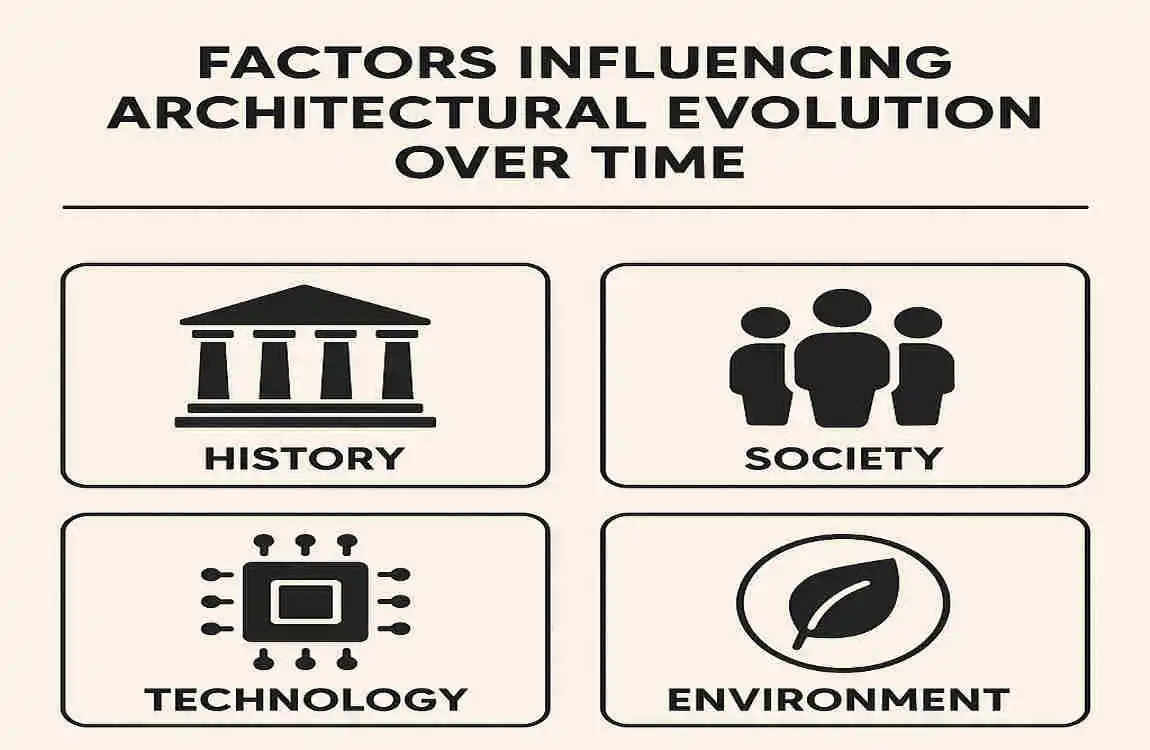
Technological Advancements
One of the key factors driving the evolution of house architecture has been technological advancements. From the development of new materials like concrete and steel to the rise of digital design tools and 3D printing, technology has opened up new possibilities for architectural design and construction.
Cultural and Social Changes
Cultural and social changes have also played a significant role in shaping house architecture over time. Shifts in family structure, lifestyle, and values have led to changes in the way we design and use our homes. For example, the rise of the nuclear family in the 20th century led to a demand for smaller, more private homes. At the same time, the growing importance of sustainability has driven a shift towards eco-friendly designs.
Environmental Considerations
Environmental considerations have become increasingly important in recent years, influencing everything from the materials used in construction to the orientation and layout of homes. In regions with harsh climates, for example, homes may be designed to maximize insulation and minimize heat loss, while in areas prone to natural disasters, resilience and durability may be key considerations.
Economic and Political Influences
Economic and political factors have also shaped the evolution of house architecture. Wars, economic booms and busts, and shifts in government policy have all had an impact on the way homes are designed and built. For example, the post-World War II housing boom in many countries led to the rapid development of new suburbs and housing styles. At the same time, government regulations and incentives have played a role in promoting sustainable and affordable housing.
How Has House Architecture Changed Over Time: Summary of Key Trends
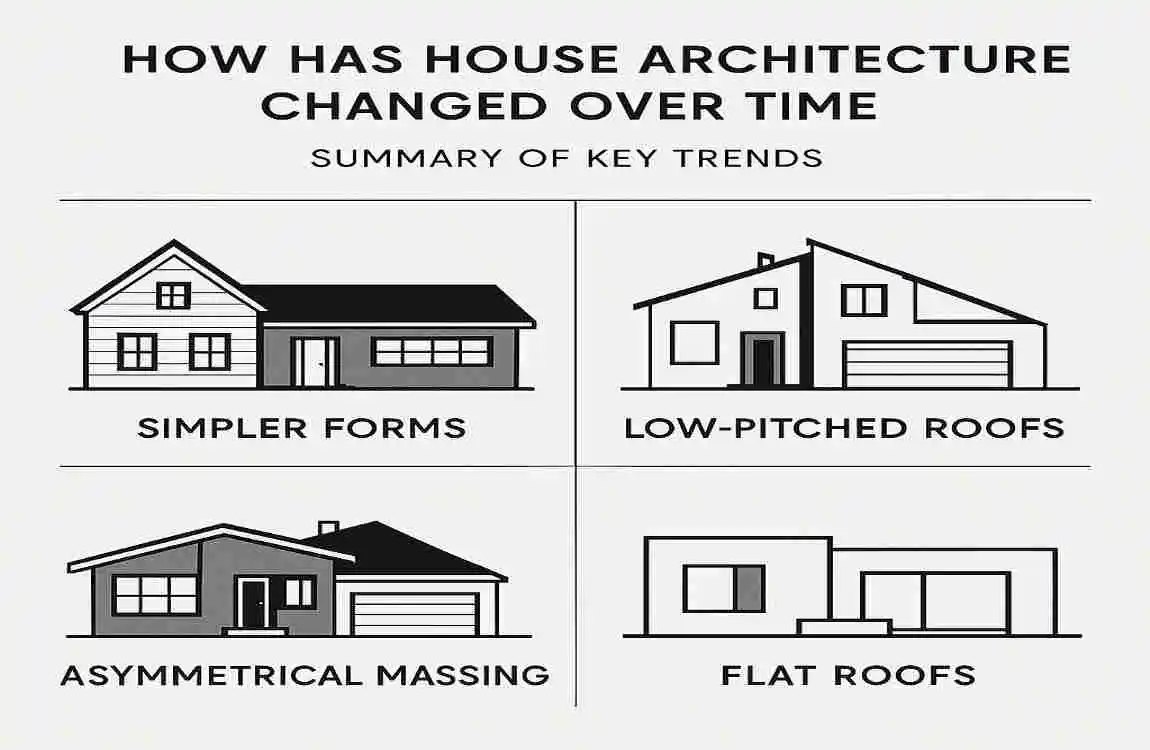
So, how has house architecture changed over time? From the earliest caves and huts to the smart, sustainable homes of today, we’ve seen a remarkable evolution in the way we design and build our living spaces. Some of the key trends we’ve explored include:
- A shift from survival-focused shelters to more permanent and sophisticated homes
- The emergence of distinct architectural styles influenced by religion, social hierarchy, and cultural values
- The rise of new materials and technologies has opened up new possibilities for design and construction
- A growing focus on sustainability, energy efficiency, and integration with nature
- The ongoing balance between function, aesthetics, and social meaning in house design
As we look to the future, it’s clear that the past will continue to influence the development of new housing styles and technologies. By understanding the history of house architecture, we can better appreciate the homes we live in today and work towards creating even better living spaces for generations to come.
How Has House Architecture Changed Over Time FAQ
How did ancient homes differ from modern houses?
Ancient homes were built purely for survival and protection, using only locally available materials like mud, stone, wood, and animal hides. Early dwellings like caves, mud huts, and simple wooden structures focused on basic shelter from weather and predators rather than comfort or aesthetics.
The biggest difference was the lack of specialized rooms. Ancient homes typically consisted of one or two multi-purpose spaces where families cooked, ate, slept, and worked. Windows were rare or small to maintain security and warmth. Sanitation happened outside, and water had to be carried in from wells or streams.
Modern homes feature complex systems ancient builders couldn’t imagine – electricity, plumbing, HVAC, and smart technology. We have dedicated spaces for specific activities and prioritize comfort, privacy, and personal expression through design.
What major architectural periods shaped residential design?
Classical architecture (500 BC – 500 AD) introduced concepts of proportion, symmetry, and decorative elements that still influence homes today. Greek and Roman innovations like columns, arches, and concrete revolutionized building possibilities.
The Medieval period (500-1500 AD) saw the rise of timber-framed houses with wattle and daub walls. Homes became more vertical, with upper floors jutting over streets. Fireplaces replaced central fire pits, dramatically improving indoor air quality.
Renaissance architecture (1400-1600) brought mathematical precision and classical revival to home design. Windows became larger, rooms more numerous, and decorative elements more refined. The concept of architectural planning emerged.
The Industrial Revolution (1760-1840) transformed everything. Mass-produced materials like steel and glass enabled entirely new building methods. Victorian homes showcased elaborate ornamentation possible with machine-cut details. Indoor plumbing and gas lighting became standard in wealthy homes.
Modern architecture (1900-present) embraced simplicity, functionality, and new materials like reinforced concrete. Styles evolved from Art Deco to Mid-Century Modern to today’s sustainable and smart homes.
How did technology change home construction?
The invention of central heating in the early 1900s revolutionized home layouts. Without needing fireplaces in every room, architects could design more open, flexible spaces. Homes could be built in colder climates with large windows and open floor plans.
Electricity’s arrival (1880s-1920s) transformed daily life and home design. Electric lighting eliminated the need for homes to maximize natural light, allowing for deeper floor plans and basements. Appliances changed kitchen design, and power outlets became essential architectural considerations.
The development of air conditioning (1950s-60s) enabled the population boom in hot climates like Florida and Arizona. Home designs could ignore natural cooling strategies, leading to different architectural styles in traditionally inhospitable areas.
Modern materials created new possibilities:
- Steel frames allowed for larger open spaces and taller structures
- Drywall replaced plaster, making construction faster and cheaper
- Synthetic insulation improved energy efficiency
- Engineered lumber enabled longer spans and unique designs
What drove the shift from closed to open floor plans?
Victorian homes (1840-1910) featured highly compartmentalized layouts with specific rooms for every function – parlor, drawing room, morning room, library. This reflected both heating limitations and social customs about formal spaces and servant areas.
The Craftsman movement (1905-1930) began breaking down barriers, promoting more casual living with connected spaces. Frank Lloyd Wright’s Prairie School designs pioneered flowing interiors where rooms merged into each other.
Post-WWII suburban homes embraced open concepts for practical reasons. Smaller homes felt larger without walls, construction costs decreased, and young families preferred casual layouts where parents could supervise children while cooking. The 1950s ranch house epitomized this trend.
Today’s preference for open floor plans reflects modern lifestyle changes – casual entertaining, family togetherness, and the desire for natural light. However, the COVID-19 pandemic has renewed interest in defined spaces for remote work and privacy.