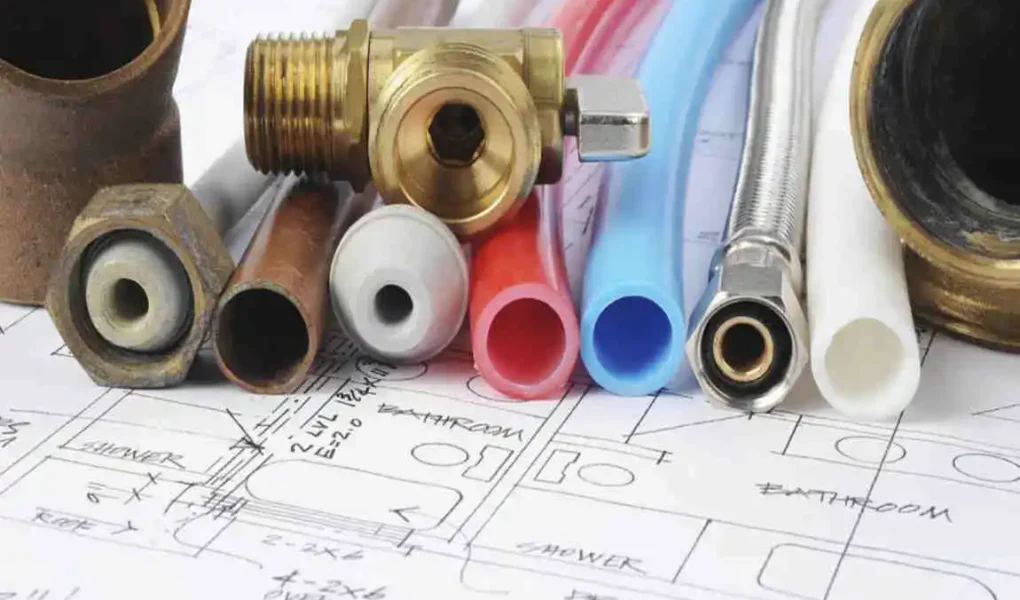
PEX plumbing, made from flexible cross-linked polyethylene, revolutionized home water systems starting in the 1980s in the U.S. Originating in the 1960s in Europe, it quickly became popular for its durability, corrosion resistance, and ease of installation in residential construction. Today, PEX dominates new home plumbing due to its flexibility and cost efficiency, offering a reliable modern alternative to copper and PVC pipes. This guide will explore its history, benefits, types, and installation in new houses.
What Is PEX Plumbing?
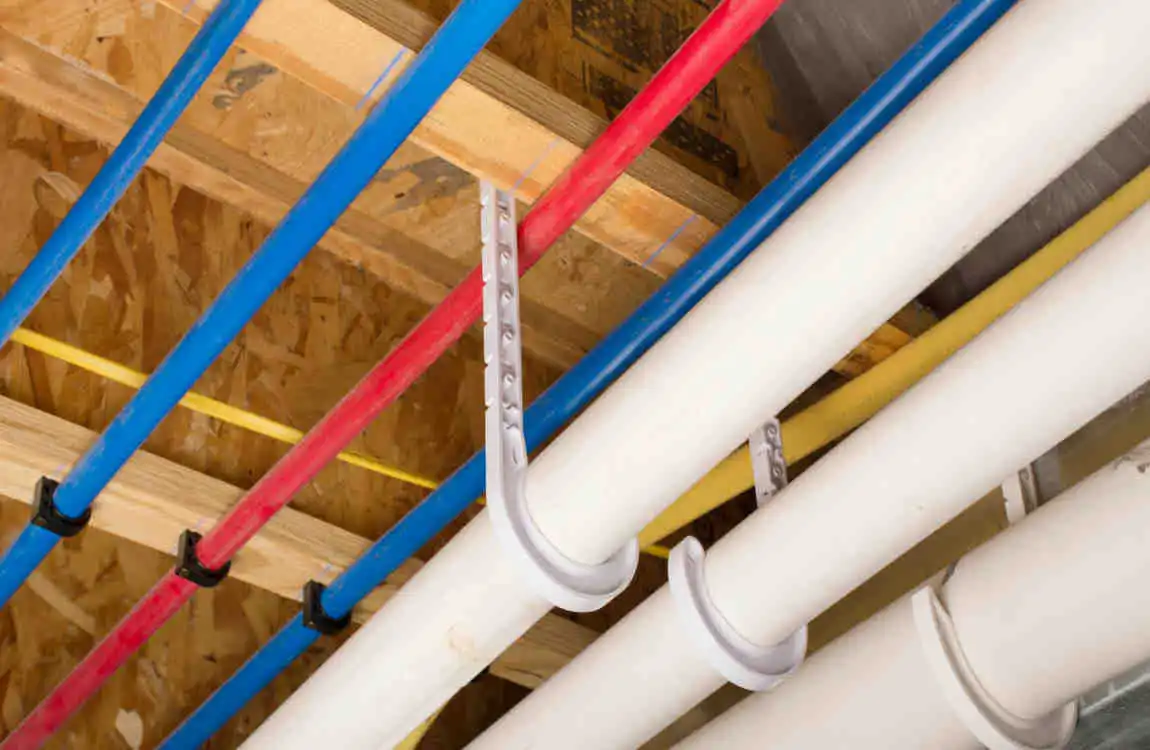

Understanding the Basics
PEX stands for cross-linked polyethylene, a type of plastic tubing that’s become increasingly popular in residential plumbing. Unlike rigid pipes, PEX tubing bends and flexes, making it highly versatile for a wide range of plumbing applications.
Think of PEX as the modern evolution of plumbing materials. Where traditional copper pipes require soldering and precise measurements, PEX offers a more forgiving and adaptable solution. The material undergoes a special manufacturing process called cross-linking, which creates molecular bonds that give the tubing its remarkable properties.
How PEX Compares to Traditional Materials
When you compare PEX to copper pipes or CPVC (chlorinated polyvinyl chloride), several differences become immediately apparent. Copper pipes have been the gold standard for decades, known for their durability and reliability. However, they’re expensive, require skilled labor for installation, and can develop pinhole leaks over time.
CPVC pipes offer a plastic alternative to copper, but remain rigid and require glue joints that can fail. They’re also sensitive to certain chemicals and can become brittle with age.
PEX tubing combines the best of both worlds. It offers the durability homeowners expect, the flexibility contractors appreciate, and the cost-effectiveness that makes new home construction more affordable.
Key Properties That Make PEX Special
The remarkable properties of PEX tubing stem from its unique molecular structure. The cross-linking process creates a three-dimensional network of polymer chains, resulting in:
Exceptional flexibility allows PEX to bend around corners without the need for elbow fittings. This means fewer connection points and reduced chances of leaks.
Superior durability ensures the material can withstand pressure fluctuations and temperature changes without degrading. The tubing maintains its integrity for decades under normal use conditions.
Corrosion resistance eliminates the mineral buildup and pitting that plague metal pipes. You won’t see the green patina or rust stains that often accompany aging copper or galvanized steel pipes.
The History of PEX Plumbing
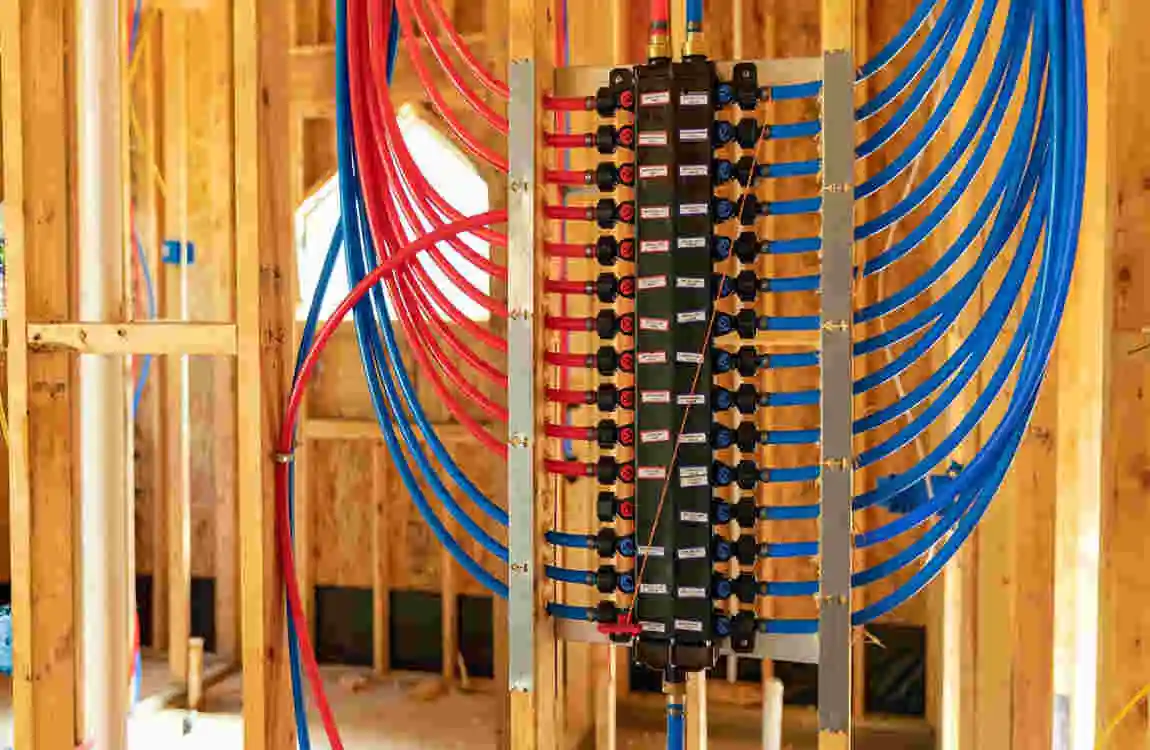

The Birth of a Revolutionary Material
The story of PEX begins in the 1960s when European scientists first developed cross-linked polyethylene. Initially, this innovative material wasn’t intended for plumbing at all. Engineers used it for industrial applications, including wire insulation and chemical transport.
German chemist Thomas Engel pioneered the cross-linking process in 1968, creating what we now know as PEX-A through the Engel method. This breakthrough opened the door to various applications, though residential plumbing wasn’t immediately on the radar.
From Industrial to Residential Applications
Throughout the 1970s, PEX found its way into European heating systems, particularly in Scandinavia and Germany. These countries embraced radiant floor heating, and PEX proved perfect for the job. The material could withstand hot-water circulation while maintaining flexibility for installation beneath floors.
The success in heating applications demonstrated PEX’s potential for broader plumbing use. European manufacturers began refining the material and developing specialized fittings for water supply systems.
What Year Did PEX Home Plumbing Start?
The answer to “what year did PEX home plumbing start?” varies by region. In Europe, residential PEX plumbing systems appeared in the early 1970s. However, the North American market tells a different story.
PEX made its North American debut in the early 1980s, primarily for radiant heating systems. The material faced significant regulatory hurdles for potable water use, as building codes and standards needed to be updated to accommodate this new technology.
The breakthrough year for widespread residential adoption in the United States was 1995, when principal plumbing codes began accepting PEX for water distribution. California, often a trendsetter in building standards, didn’t approve PEX for residential use until 2010, making it one of the last states to embrace the technology.
Major Milestones in PEX Adoption
YearMilestone
1968 Thomas Engel develops the PEX-A cross-linking method
1972 First residential PEX installations in Europe
1984, PEX was introduced to the North American market for heating
1995 Major U.S. plumbing codes approve PEX for water supply
The 2006 International Residential Code includes PEX standards
In 2010, California approved PEX for residential plumbing
2015 PEX becomes the most installed plumbing material in new U.S. homes
How PEX Plumbing Became Popular in New Houses
The Perfect Storm of Factors
Several factors converged to make PEX the preferred choice for new home construction. The housing boom of the early 2000s created demand for faster, more efficient building methods. Builders needed materials that could speed up construction without sacrificing quality.
Labor shortages in skilled trades also played a crucial role. Finding experienced plumbers who could solder copper pipes became increasingly difficult and expensive. PEX offered a solution that required less specialized skill while maintaining professional standards.
The rising cost of copper further accelerated PEX adoption. As copper prices soared due to global demand, builders sought cost-effective alternatives that wouldn’t compromise on performance.
Building Code Evolution
The journey toward widespread PEX acceptance involved extensive testing and lobbying by manufacturers. Industry organizations worked tirelessly to demonstrate PEX’s safety and reliability to code officials.
The International Association of Plumbing and Mechanical Officials (IAPMO) played a pivotal role in establishing standards for PEX systems. Their Uniform Plumbing Code amendments paved the way for broader acceptance.
State-by-state adoption created a patchwork of regulations that gradually unified. Early adopter states like Texas and Arizona showed that PEX could perform exceptionally well, even in challenging climates.
Industry Innovation and Endorsements
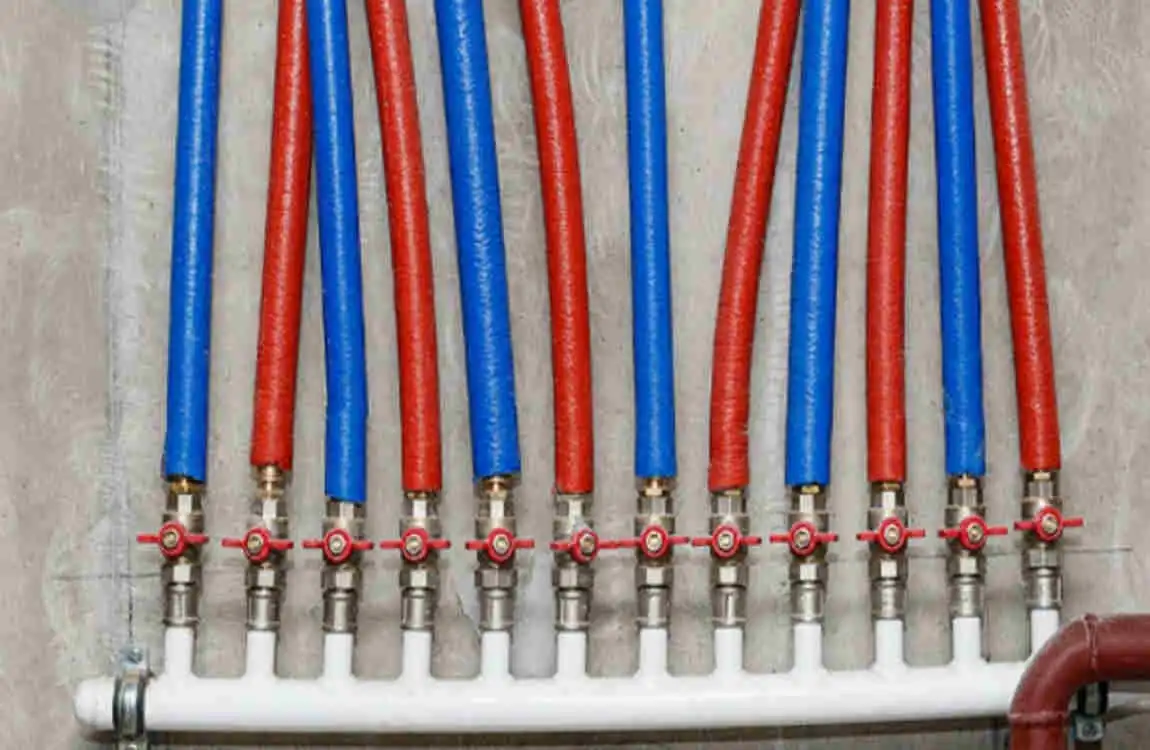
Manufacturers didn’t just wait for acceptance; they actively improved their products. New fitting systems made connections more reliable. Color-coding (red for hot, blue for cold) simplified installation and reduced errors.
Professional organizations began endorsing PEX after seeing its performance in the field. The National Association of Home Builders recognized PEX’s contribution to efficient construction, while plumbing contractors appreciated the reduced callback rates.
Benefits of Using PEX Plumbing in New Homes
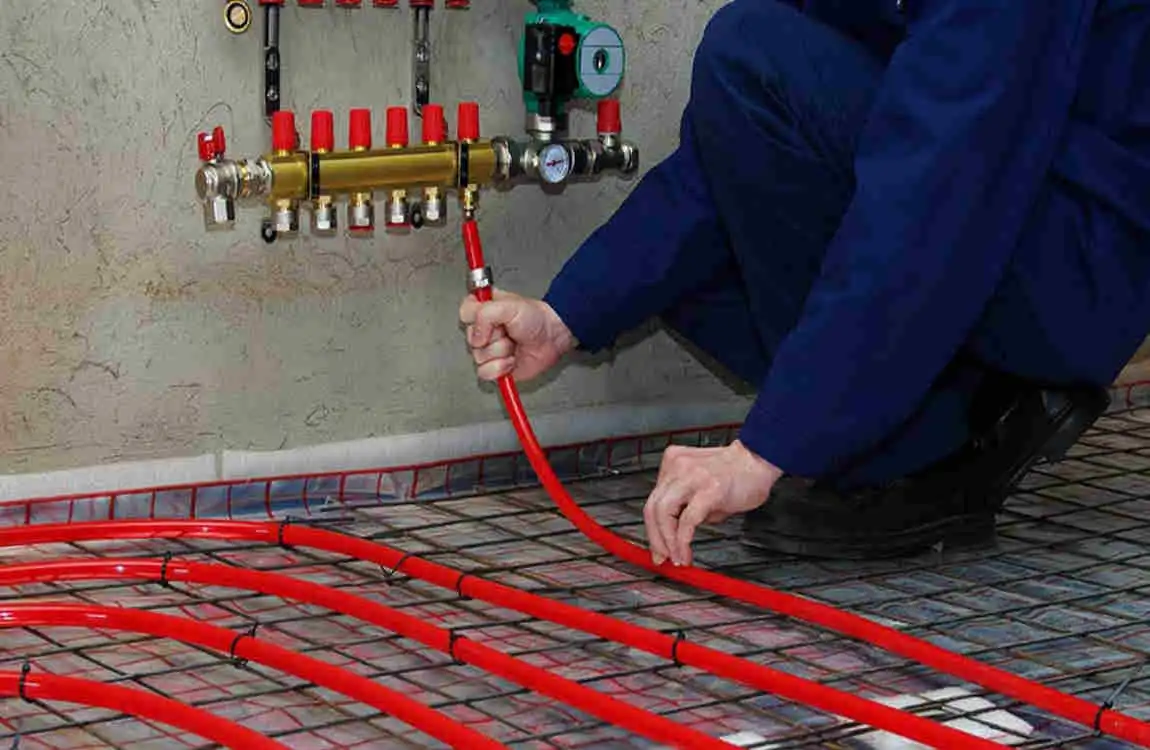

Significant Cost Savings
When you examine the total cost of a plumbing system, PEX offers substantial savings across multiple areas:
Material costs are typically 25-30% lower than for copper for the same application. The tubing itself is less expensive, and you need fewer fittings since PEX can bend around corners.
Labor costs decrease dramatically because installation goes faster. A plumber can rough-in a typical new home with PEX in half the time required for copper. This efficiency translates directly to lower costs for builders and homeowners.
Long-term savings come from reduced maintenance and fewer repairs. PEX systems have fewer joints, reducing the potential for leaks. The material’s resistance to corrosion and scaling means consistent water flow over decades.
Superior Freeze Resistance
One of PEX’s most remarkable properties is its ability to expand when water freezes inside it. While copper pipes burst when water freezes and expands, PEX can stretch to accommodate the ice, then return to its original shape when thawed.
This doesn’t mean PEX is freeze-proof – extreme conditions can still cause damage. However, the material provides significantly better protection against freeze-related failures, particularly valuable in vacation homes or properties in cold climates.
Longevity and Low Maintenance
Modern PEX systems are designed to last 50 years or more under normal conditions. The material doesn’t corrode, pit, or develop pinhole leaks like copper. It resists scale buildup, maintaining consistent water flow throughout its lifespan.
Maintenance requirements are minimal. There’s no need for periodic inspections for corrosion or replacement of sacrificial anodes. The smooth interior surface of PEX tubing helps prevent biofilm formation, improving water quality.
Quieter Operation
Have you ever heard pipes banging when someone turns off a faucet quickly? That’s called water hammer, and PEX naturally dampens this effect. The material’s flexibility absorbs pressure waves, reducing noise in plumbing systems.
The reduced noise isn’t just about comfort – it also indicates less stress on the system. This gentler operation extends the lifespan of fixtures and connections throughout the plumbing network.




