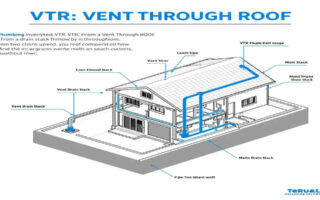
Rerouting your home plumbing system can feel like a daunting task, but when done correctly, it can significantly improve your home’s functionality and value. Whether you’re remodelling, repairing damaged pipes, or upgrading for efficiency, rerouting plumbing requires careful planning, the right materials, and attention to safety.
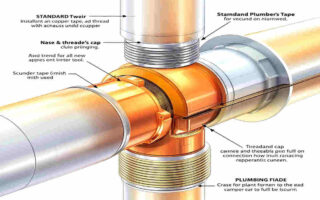
Why Rerouting Plumbing is Necessary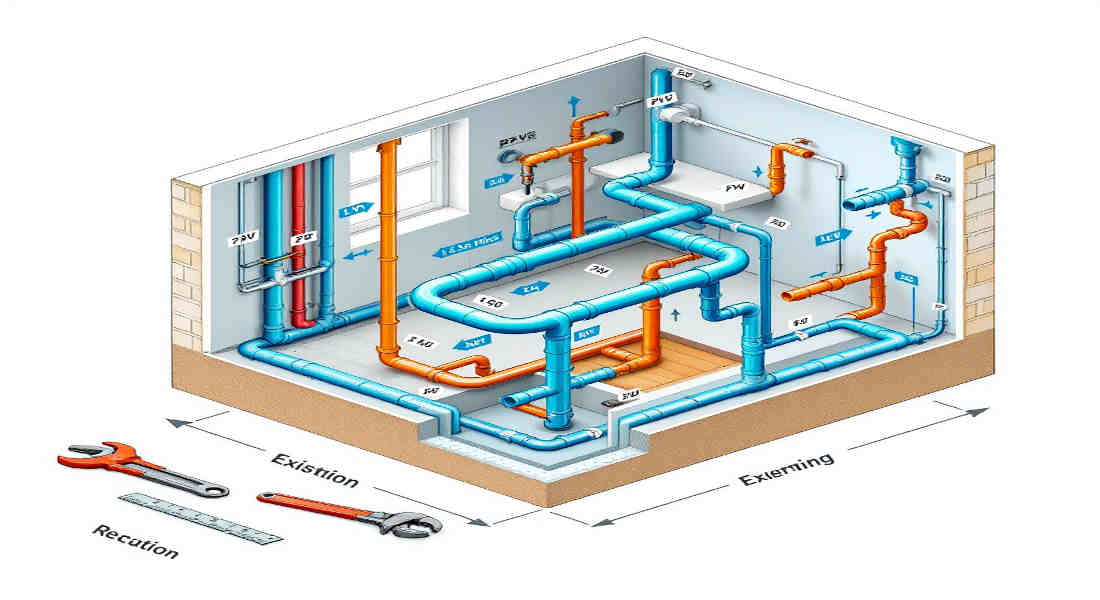
Rerouting plumbing isn’t something homeowners typically think about until it’s absolutely necessary. You might need to reroute your plumbing for several reasons:
- Home renovations: Adding new rooms or moving fixtures like sinks or toilets often requires rerouting pipes to connect to your existing system.
- Damaged pipes: Pipes may become corroded or leak over time, making rerouting a viable solution to avoid future issues.
- Improving efficiency: Sometimes, the original plumbing layout isn’t optimized for modern systems, and rerouting can help improve water flow and energy efficiency.
However, rerouting plumbing is not a task to take lightly. Without proper planning and execution, you risk costly repairs, leaks, or even structural damage. The goal of this guide is to help you understand the process and execute it safely and effectively.
Understanding Home Plumbing Systems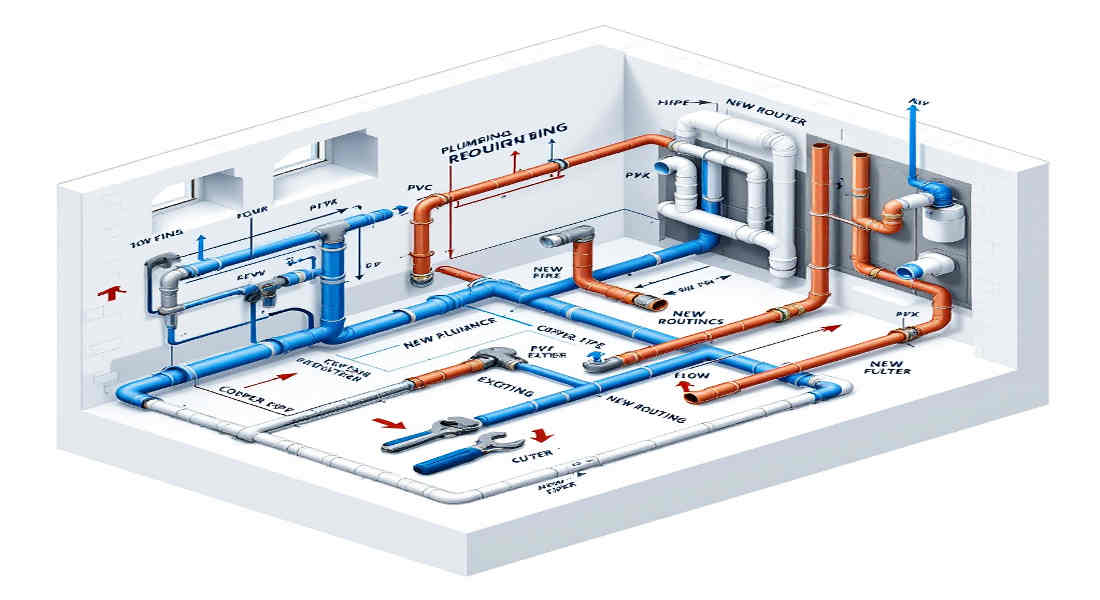
Before you start rerouting your plumbing, it’s essential to understand how your home’s plumbing system works. Knowledge of the system is your first step toward making informed decisions.
You may also read (first install indoor plumbing).
Components of a Home Plumbing System
A home plumbing system is made up of three main components:
- Water supply lines: These pipes bring clean water into your home.
- Drain pipes: These carry wastewater out of your home to the sewer or septic system.
- Fixtures: Faucets, sinks, toilets, and appliances like dishwashers or washing machines connect to both the water supply and drainage lines.
Assess Your Existing Plumbing Layout
To reroute plumbing safely, you must first understand your current setup:
- Locate the main water supply valve: This is usually near the water meter or in the basement. It’s essential to know where this is to shut off water during the rerouting process.
- Trace sewer lines and drainage paths: Knowing where your wastewater exits the home is just as important as identifying your water supply lines.
Why Reroute Plumbing?
Here are some common scenarios that require rerouting:
- Damaged or leaking pipes: If pipes are beyond repair, rerouting can be more effective than patching.
- Remodelling projects: Moving a kitchen or bathroom often requires rerouting the plumbing lines to fit the new layout.
- Adding fixtures: Installing a new sink, toilet, or shower means extending the plumbing system to accommodate the new fixture.
Planning Your Plumbing Reroute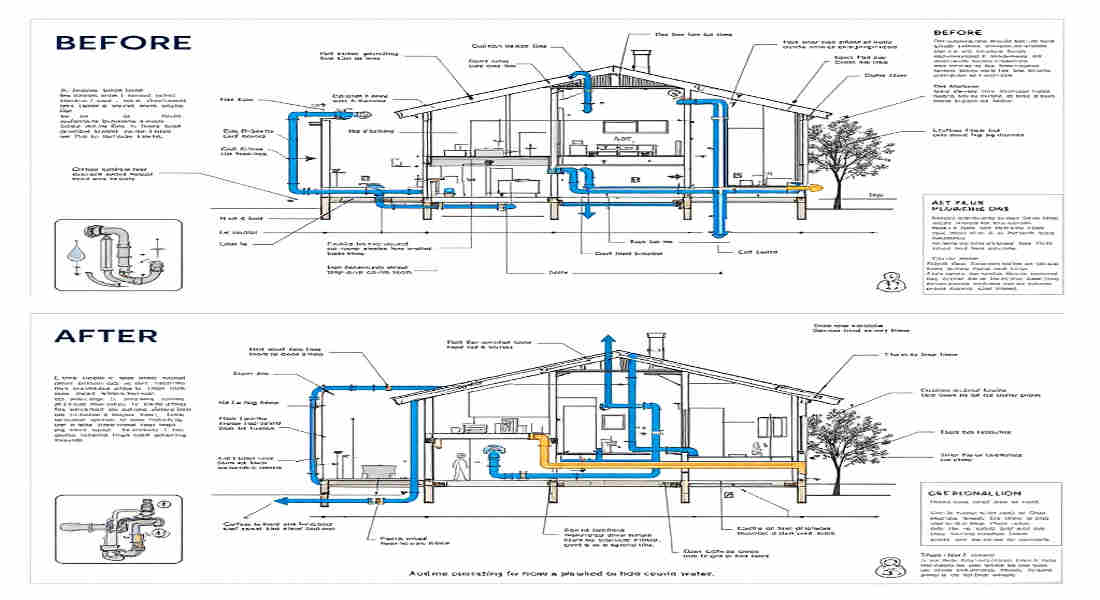
Planning is the foundation of a successful plumbing reroute. A poorly planned reroute can lead to costly mistakes, so take the time to map everything out.
Assess the Current Layout
- Start by sketching the existing plumbing layout. Identify which pipes need to be moved and which can remain.
- Take note of the locations of fixtures, supply lines, and drainpipes.
You may also read (santee in home plumbing).
Identify the New Layout
- Decide where the new pipes will go and how they’ll connect to your existing system.
- Avoid placing pipes in exterior walls in cold climates, as this increases the risk of freezing.
- Look for the path of least resistance to avoid unnecessary cutting into walls, floors, or ceilings.
Comply with Building Codes
- Every city or county has its own building codes and permits for plumbing work. Research these requirements to avoid fines or legal issues.
- If you’re unsure about code compliance, consider consulting with a licensed plumber or local building inspector.
Avoid Structural and Utility Interference
When planning your route, ensure you’re not interfering with:
- Electrical wiring: Cutting into walls may expose electrical lines.
- Gas lines: These pose a significant safety risk if damaged.
- Structural supports: Avoid cutting into load-bearing walls, beams, or joists.
Tools for Planning
To make planning easier, you can use:
- Plumbing diagrams: These visual guides help you map out the new route.
- Stud finders and pipe locators: These tools help you identify hidden structural elements and existing pipe locations.
Selecting the Right Materials for Rerouting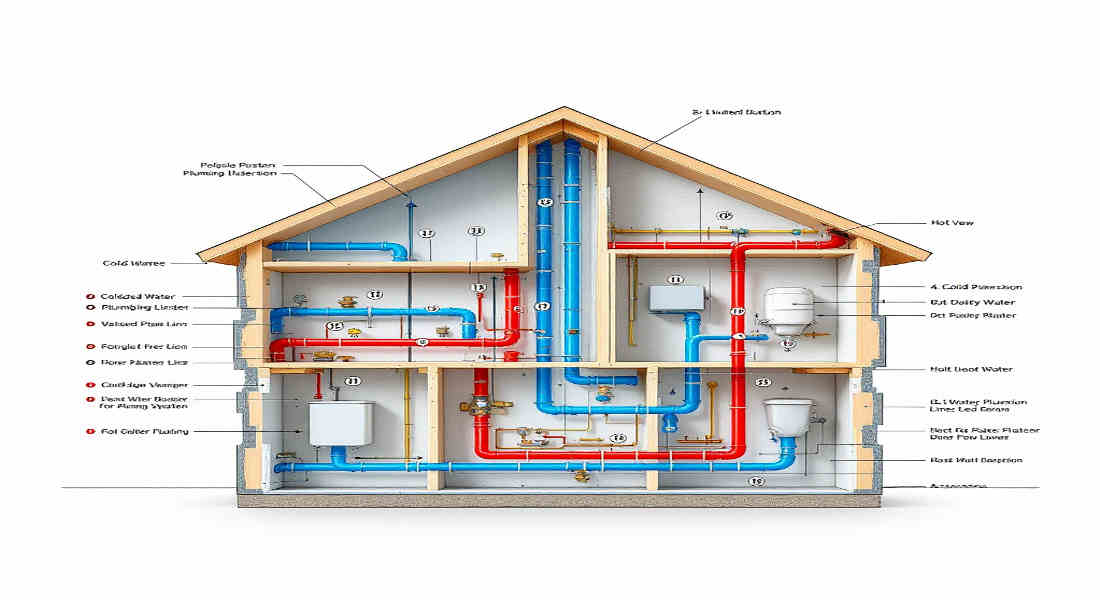
Choosing the right materials is a crucial part of rerouting plumbing. The materials you use will affect the durability, cost, and ease of installation.
Common Plumbing Materials
Here’s a breakdown of the most commonly used plumbing materials:
MaterialProsCons
Copper Durable, long-lasting, resistant to bacteria Expensive, requires soldering
PEX Flexible, easy to install, resistant to freezing, can degrade under UV exposure
PVC is Affordable, lightweight, and easy to cut. Brittle over time, not suitable for hot water
Recommended Connectors and Fittings
- SharkBite fittings: These push-to-connect fittings are popular for DIY projects because they’re easy to use and don’t require special tools.
- Couplings and elbows: These are used to connect pipes at angles or to join different pipe types.
When selecting materials, consider:
- Longevity: Will the material last for decades?
- Cost: Does it fit your budget?
- Ease of installation: Are tools or professional skills required?
Step-by-Step Guide to Rerouting Home Plumbing
Now that you’ve planned and gathered materials, it’s time to reroute your plumbing. Follow these steps for a smooth process:
Shut Off the Water Supply
Locate the main water valve and turn it off. This prevents water from flooding your workspace.
Drain the Pipes
Open all faucets to let any remaining water drain out of the pipes.
Cut and Remove Old Pipes
- A pipe cutter or saw is used to remove the sections of the pipe that need replacing.
- Be careful not to damage surrounding materials.
Drill or Cut Through Walls and Floors
- Use a stud finder to avoid hitting wires or structural supports.
- Drill holes just large enough for the new pipes.
Install New Pipes
- Follow the planned route, ensuring proper slopes for drainage.
- Use brackets or straps to secure pipes in place.
Secure Connections
- Copper pipes: Solder the joints for a watertight seal.
- PEX pipes: Use crimp rings or SharkBite fittings for secure connections.
Test the System
Turn the water back on and check for leaks or low water pressure.
Final Inspection
If your local codes require permits, schedule an inspection to ensure your work meets safety standards.
Common Challenges and How to Avoid Them
During the rerouting process, you may face several challenges. Here’s how to handle them:
Avoiding Damage to Other Utilities
- Use a pipe locator to identify hidden utility lines before cutting or drilling.
Preventing Leaks
- Test all connections before sealing walls or floors.
Working in Tight Spaces
- Use flexible PEX tubing for easier manoeuvrability in cramped areas.
When to Call a Professional
If you encounter gas lines, structural issues, or complex layouts, it’s best to hire a licensed plumber.
Benefits of Properly Rerouted Plumbing
Rerouting plumbing isn’t just about fixing issues—it comes with several long-term benefits:
- Improved water flow: A better layout ensures consistent water pressure.
- Easier maintenance: A well-organised system is easier to repair.
- Increased home value: Updated plumbing adds resale value.
- Leak prevention: Proper installation reduces the risk of future leaks.
When to Hire a Professional Plumber
Some plumbing tasks are best left to the experts. Here’s when to consider hiring a professional:
- Complex reroutes: If the layout requires extensive work.
- Code compliance: Professionals ensure everything meets local regulations.
- Safety concerns: Avoid risks like damaging gas lines or causing structural instability.
You may also read (house plumbing pipes).