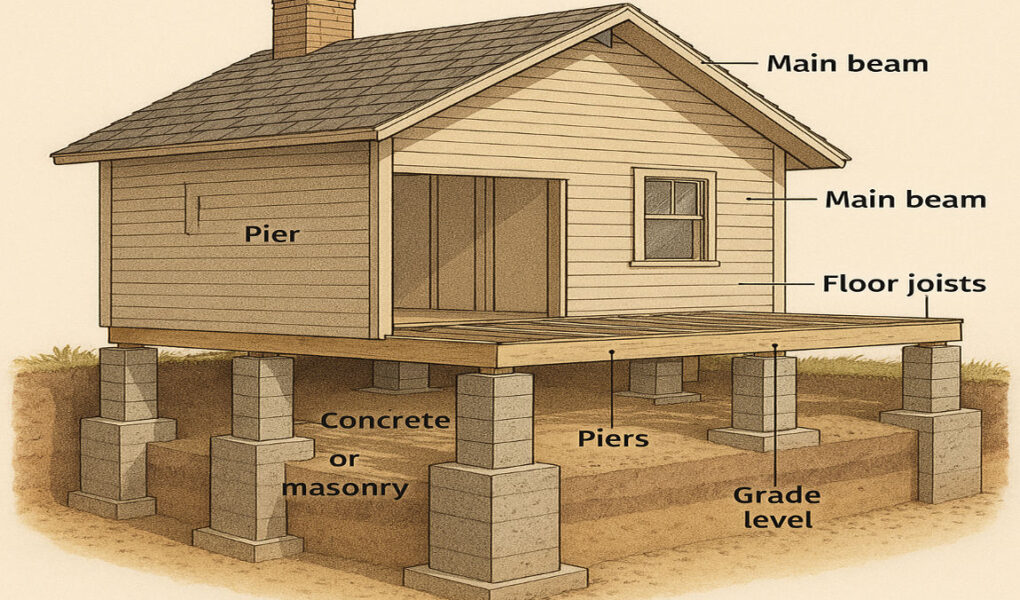
When it comes to building a home, one of the most critical aspects is ensuring that it has a strong and stable foundation. A foundation is not just a structural element; it’s the backbone of your home, providing stability, safety, and longevity. Without a solid foundation, even the most beautifully designed house can face issues such as cracks, uneven floors, or, worse, structural failure.
But did you know that not all foundations are created equal? Depending on the location, soil type, and environmental conditions, different types of foundations are used. One such foundation type is the pier foundation, which is particularly popular in specific scenarios.
What Is a Pier Foundation on a House?
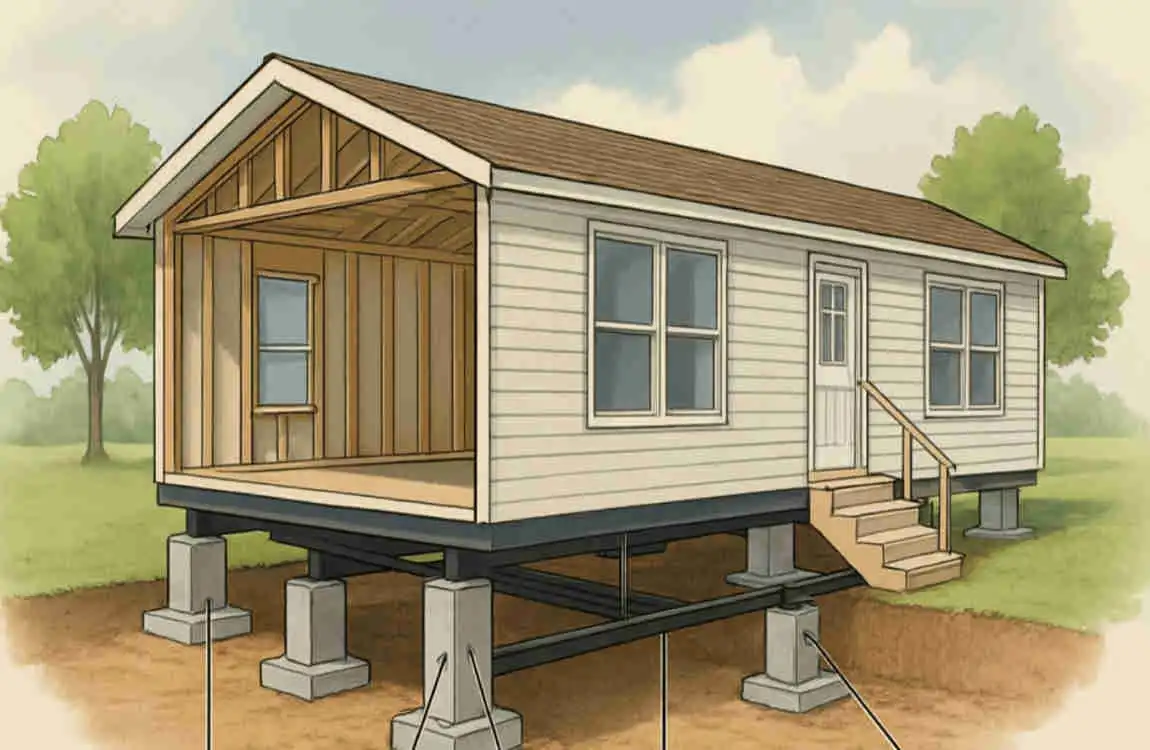
A pier foundation is a type of foundation that uses vertical supports, or piers, to elevate a structure above the ground. These piers are typically made of materials such as concrete, masonry, steel, or timber, and they are strategically placed to support the weight of the house.
How Pier Foundations Work
The primary purpose of a pier foundation is to transfer the weight of the house to the ground through these vertical supports. Unlike slab foundations, which rest directly on the ground, pier foundations create a gap or crawl space between the house and the earth. This design is instrumental in areas with uneven terrain, expansive soils, or flood-prone regions.
How Pier Foundations Differ from Other Types
Pier foundations are distinct from other foundation types like:
- Slab Foundations: These are flat concrete slabs poured directly on the ground. They are common in areas with stable soil and minimal risk of flooding.
- Crawl Space Foundations: These are similar to pier foundations but use continuous walls instead of individual piers to create a crawl space.
- Pile Foundations: These are deep foundations that use long, slender columns driven deep into the ground to support heavy loads, often used for large buildings.
Common Uses of Pier Foundations
Pier foundations are commonly used in:
- Homes near water: They elevate the structure to protect it from flooding.
- Uneven terrain: Piers can be adjusted to accommodate slopes or hills.
- Expansive soils: In areas where soil expands and contracts, pier foundations provide stability.
Visually, homes with pier foundations often resemble houses on stilts or decks, with the house structure raised above the ground.
Types of Pier Foundations
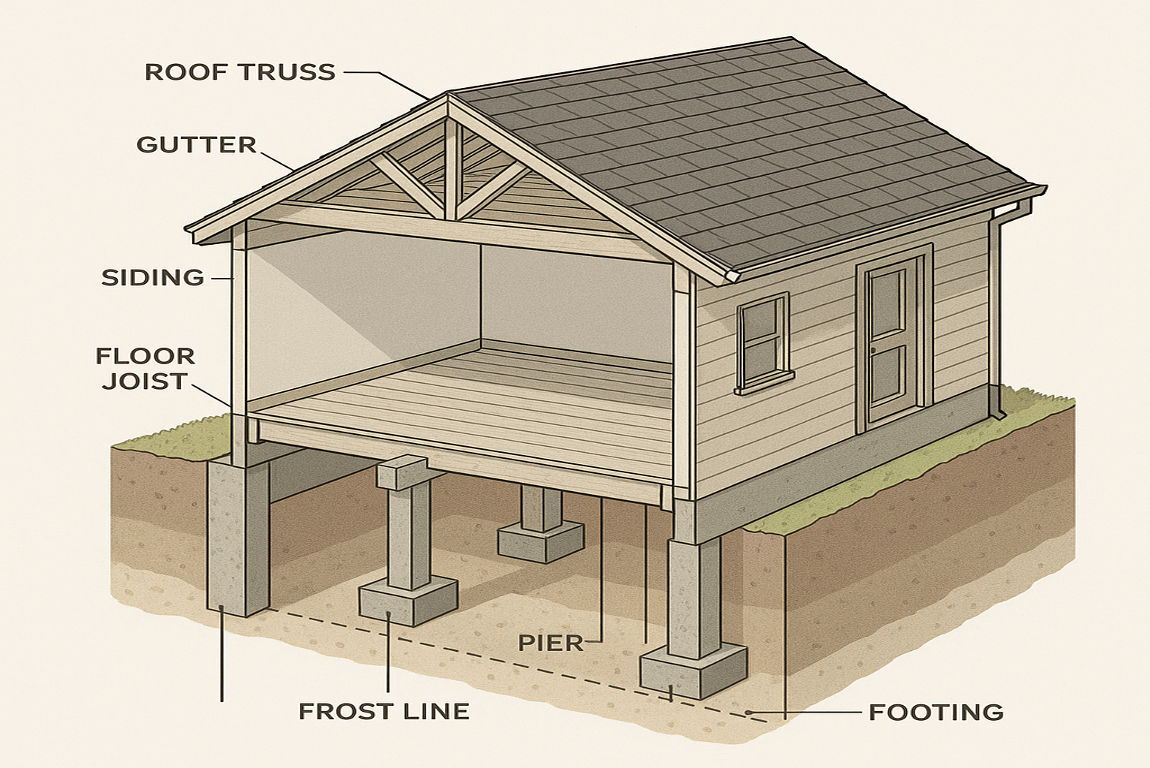
Pier foundations come in various types, each suited to specific needs and conditions. Let’s explore the most common ones:
Masonry Pier Foundation
Masonry pier foundations are constructed using materials like bricks, stones, or concrete blocks. These piers are often used for lightweight structures and in areas with good drainage.
Advantages:
- Cost-effective for small projects.
- Easy to construct with locally available materials.
Disadvantages:
- Limited load-bearing capacity.
- Vulnerable to weathering if not correctly sealed.
Concrete Pier Foundation
Concrete piers are either precast (made off-site and transported) or cast-in-place (poured directly on-site). These are among the most durable and commonly used pier types for residential buildings.
Advantages:
- High strength and durability.
- Resistant to weather and decay.
Disadvantages:
- Requires skilled labor for installation.
- It can be more expensive than masonry piers.
Drilled Pier Foundation (Caissons)
Drilled piers, also known as caissons, involve drilling deep holes into the ground and filling them with reinforced concrete. These are ideal for heavy structures or areas with unstable soil.
Advantages:
- High load-bearing capacity.
- Suitable for tall or heavy buildings.
Disadvantages:
- Complex and time-consuming construction process.
- Requires specialized equipment.
Timber Pier Foundation
Timber piers are made from treated wood and are often used for temporary structures or lightweight buildings.
Advantages:
- Cost-effective and easy to install.
- Environmentally friendly if sustainably sourced.
Disadvantages:
- Prone to decay and pest damage.
- Requires regular maintenance.
Steel Pier Foundation
Steel piers are either driven into the ground or screwed in place. They are commonly used in areas with unstable soils or for underpinning existing foundations.
Advantages:
- Quick and easy installation.
- High strength and durability.
Disadvantages:
- Susceptible to corrosion if not correctly treated.
- Higher initial cost compared to other materials.
Type Material Best For Pros Cons
Masonry Pier Bricks, stones, Light structures, good drainage Cost-effective, easy to construct, Limited load capacity, weathering
Concrete Pier Precast or cast-in-place concrete Residential homes, durable structures Strong, weather-resistant Expensive, skilled labor needed
Drilled Pier Reinforced concrete Heavy buildings, unstable soil High load capacity, stable Complex, time-consuming
Timber Pier Treated wood Temporary or light structures Affordable, eco-friendly Prone to decay, high maintenance
Steel Pier Steel Unstable soils, underpinning Durable, quick installation Corrosion risk, costly
How Are Pier Foundations Built?
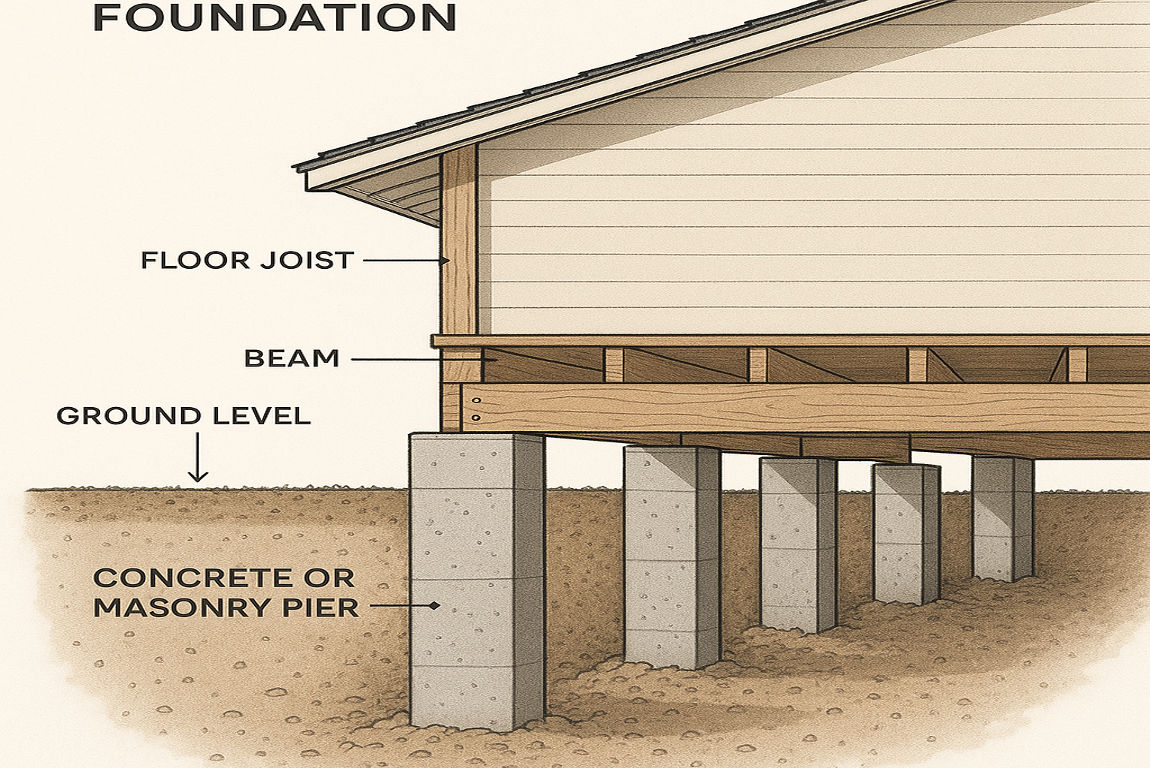
The construction of a pier foundation involves several steps, each of which is crucial to ensuring the stability and longevity of the structure.
Step-by-Step Process
- Site Preparation: The site is cleared, and the soil is tested to determine its load-bearing capacity.
- Excavation: Holes are dug at specific locations where the piers will be placed. The depth depends on the soil type and load requirements.
- Setting the Piers: Depending on the type, piers are either precast and placed into the holes or cast in place using concrete.
- Reinforcement: Steel reinforcements may be added for extra strength.
- Backfilling: The holes are filled with soil or concrete to secure the piers in place.
- Curing: If concrete is used, it is allowed to cure and harden before the structure is built on top of it.
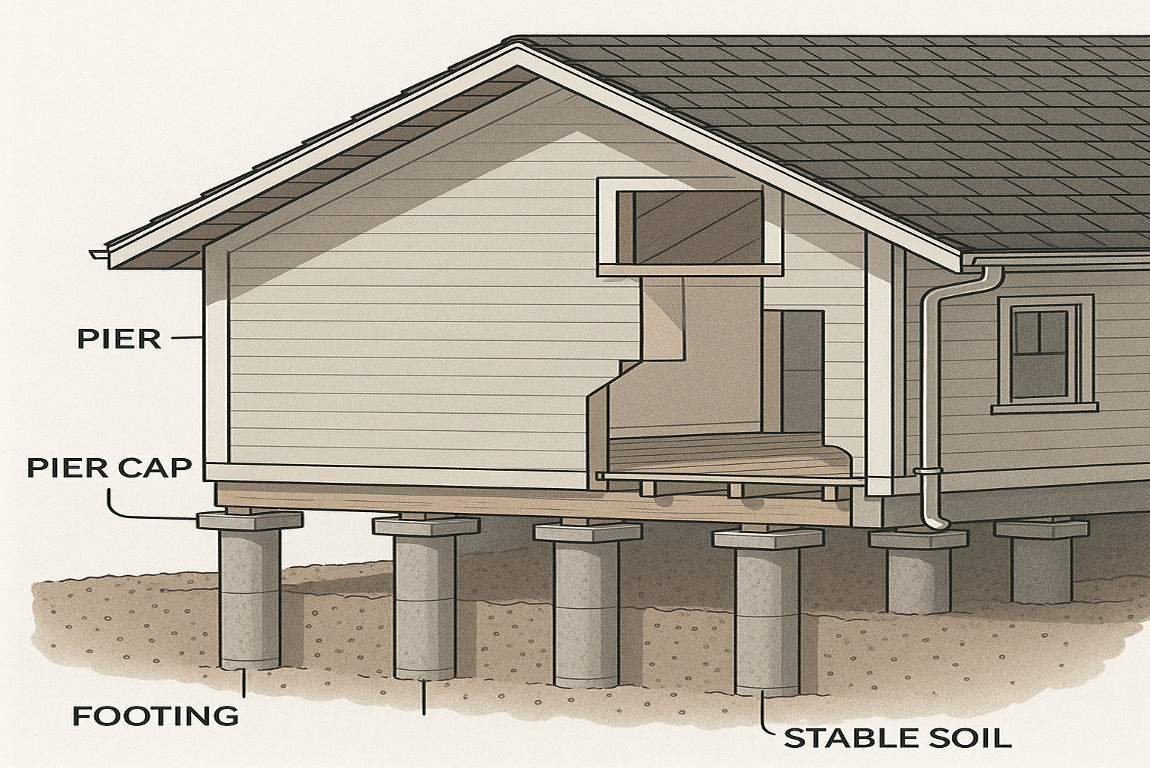
Key Considerations
- Soil Testing: Ensures the foundation is built on stable ground.
- Spacing: Piers must be evenly spaced to distribute the load evenly.
- Depth: Piers should reach a stable soil layer to prevent settling.
Advantages of Pier Foundations for Homes
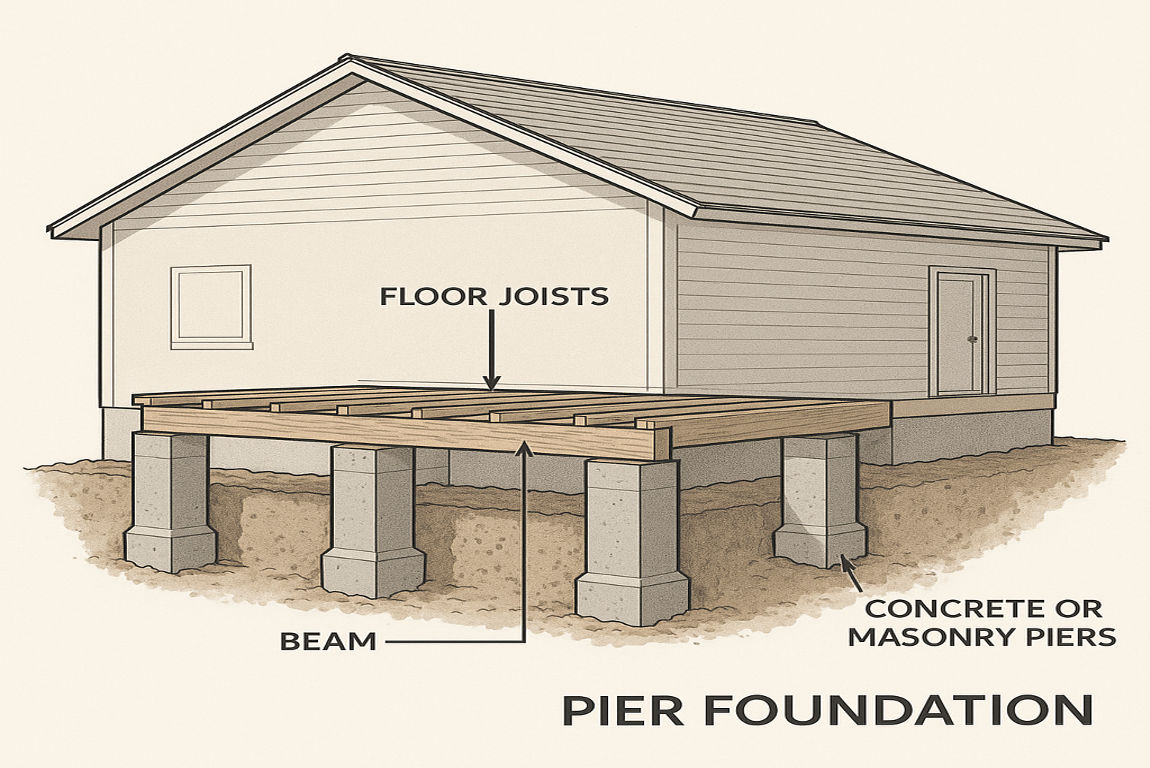
Pier foundations offer several benefits, making them a popular choice for many homeowners:
- Protection from Flooding: By elevating the house, pier foundations protect it from water damage in flood-prone areas.
- Adaptability to Uneven Terrain: They can be adjusted to accommodate slopes or hills.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Pier foundations are often cheaper than full basement or slab foundations.
- Ease of Access: The crawl space allows for easy access to plumbing, wiring, and other utilities.
- Reduced Construction Time: They require less excavation and labor compared to other foundation types.
Potential Drawbacks and Considerations
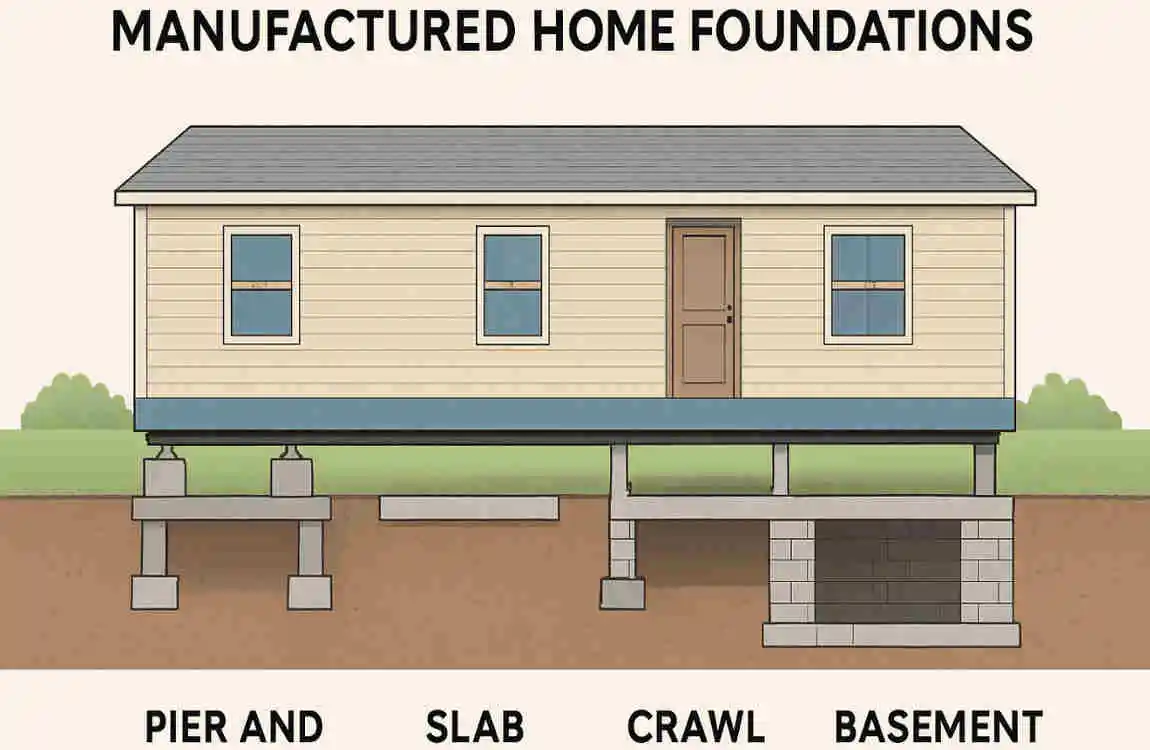
While pier foundations have many advantages, they also come with some drawbacks:
- Limited Load Capacity: They may not be suitable for very heavy or high-rise buildings.
- Maintenance Needs: Timber piers, in particular, require regular upkeep to prevent decay.
- Pest Vulnerability: If not properly sealed, the crawl space can attract pests.
- Moisture Issues: Proper drainage and sealing are essential to avoid moisture buildup.
When to Choose a Pier Foundation for Your Home

Pier foundations are ideal in the following scenarios:
- Flood-Prone Areas: They elevate the modern house above potential flood levels.
- Uneven Terrain: They can be customized to suit sloped or hilly sites.
- Expansive Soils: They provide stability in areas where soil expands and contracts.
Frequently Asked Questions About Pier Foundations on a House
What is a Pier Foundation?
A pier foundation is a type of foundation that uses vertical columns or piers to support the structure of a house. These piers transfer the building’s load to the soil below, creating a space underneath the house often referred to as a crawl space . This type of foundation is also known as a pier and beam foundation, where beams are built on top of the piers to support the house .
When is a Pier Foundation Used?
Pier foundations are commonly used in areas with sloping terrain or expansive soils that can shift or settle over time . They are also popular in coastal regions where rising tides and flooding are concerns, as the piers lift the house off the ground and protect it from water damage .
What are the Advantages of a Pier Foundation?
- Cost-effective: Pier foundations may cost less than other types of foundations.
- Flood protection: By elevating the house, pier foundations help protect against flooding and rising tides .
- Easier access: The crawl space created by pier foundations allows for easier access to plumbing, wiring, and ductwork .
- Improved ventilation: Air circulation under the house reduces the risk of mildew and rot .
What are the Disadvantages of a Pier Foundation?
- Insulation challenges: Floors must be heavily insulated to prevent heat loss and protect against critters .
- Vulnerability to damage: If one pier or post is damaged, it can lead to significant damage to the overall foundation .
- Exposure to elements: The under-floor area must be protected from the elements to prevent damage .
How is a Pier Foundation Constructed?
A pier foundation is typically constructed using large diameter cylindrical columns made of concrete or other materials. These piers are driven deep into the ground until they reach firm strata, providing a stable base for the house . Rebar and concrete beams are then placed on top of the piers to support the structure .
Can a Pier Foundation be Used for Any Type of House?
While pier foundations are versatile and can be used for various types of houses, they are most suitable for homes in specific conditions, such as sloping lots, expansive soils, or coastal areas prone to flooding. It’s essential to consult with a structural engineer or foundation specialist to determine if a pier foundation is appropriate for your specific location and house design.
How Much Does a Pier Foundation Cost?
The cost of a pier foundation can vary depending on factors such as the size of the house, the number of piers required, and the local soil conditions. On average, pier foundations may be less expensive than other types of foundations, but it’s best to obtain quotes from multiple contractors to get an accurate estimate for your specific project .
How Long Does a Pier Foundation Last?
With proper maintenance and care, a well-constructed pier foundation can last for many decades. Regular inspections and repairs, if necessary, can help extend the life of the foundation and ensure the stability of your home.