You’ve finally found the perfect house. It has the wrap-around porch you’ve always wanted, the kitchen is modern, and the neighborhood is quiet. You’ve saved up your down payment, and you’re ready to sign. But then, you get the call from the bank. Your mortgage application was denied. Maybe it’s because your credit score is a few points too low, or perhaps because you’re self-employed and your income looks “unstable” on paper.
In the real estate market of 2026, this is a reality for millions. With average mortgage rates hovering around 7.5% and banks tightening their lending belts, traditional financing feels like an exclusive club that’s hard to join. But what if I told you that you don’t actually need a bank to buy a home?
What Is In-House Financing Real Estate?

To put it simply, in-house real estate financing is a setup in which the seller of the property—rather than a traditional bank or mortgage company—provides the loan to the buyer. Instead of sending a monthly check to a massive financial institution like Chase or Wells Fargo, you send your payment directly to the seller or a specialized company they use to manage the loan.
Think of it like buying a car at a “Buy Here, Pay Here” lot, but for a house. You are cutting out the middleman. This method is often referred to as seller financing, owner financing, or dealer financing.
The Core Difference: Bank vs. In-House
When you go to a bank, they look at you as a set of data points: your debt-to-income ratio, your FICO score, and your employment history. If you don’t fit their rigid “box,” you’re out.
In-house financing is different. The seller is usually more interested in your down payment and your ability to make the monthly payments than a perfect credit score. They have the house; you want the house; and together, you create a private contract to make the deal happen.
Common Types of In-House Financing
Not all in-house deals look the same. Depending on who you are buying from, the structure might change:
- Seller Financing (Owner-Financed Homes): This is the most common type. An individual homeowner who owns their property outright (or has significant equity) decides to “be the bank.” They sell you the home, and you pay them back over time with interest.
- Builder or Developer Financing: Large home-building companies often have their own lending arms. They want to move their inventory quickly, so they offer “in-house” loans to buyers who might not qualify for traditional mortgages.
- Dealer Financing (Mobile and Modular Homes): If you are looking at manufactured housing, dealerships almost always offer in-house financing. It is often the fastest way to get into a home in that specific market.
A Quick Comparison at a Glance
FeatureIn-House FinancingTraditional Bank Mortgage
Approval Speed Extremely Fast (Days) Slow (30–60 Days)
Credit Score Flexible / Low Scores OK Strict (Usually 620+)
Down Payment Negotiable (Often 10-20%) Variable (3% to 20%+)
Closing Costs Low / Minimal High (Thousands of dollars)
Interest Rates Usually Higher (8-12%) Market Standard (6-7.5%)
How Does In-House Financing Real Estate Work?
You might be wondering, “How do we actually make this legal?” It’s not just a handshake deal. In-house financing involves specific legal documents that protect both you and the seller.
The Step-by-Step Process
If you’re interested in no-bank home buying, here is the general path you’ll take:
- Find the Right Property: Look for listings that specifically mention “owner financing,” “seller will carry,” or “in-house financing available.”
- Negotiate the Terms: Since there is no bank setting the rules, everything is up for debate. You’ll discuss the interest rate, monthly payment, and loan duration.
- The Down Payment: This is your leverage. A larger down payment (often 10% to 20%) makes a seller much more likely to trust you, even if your credit isn’t great.
- Sign the Legal Docs: You will sign a Promissory Note (your promise to pay) and a Deed of Trust or a Mortgage (the document that gives the seller the right to take the house back if you don’t pay).
- Closing the Deal: You’ll usually close through a title company or an attorney to ensure the title is clear. You get the keys, and the seller receives your monthly payments.
Understanding the “Balloon Payment”
One thing you must watch out for in in-house financing real estate is the balloon payment. Many sellers don’t want to wait 30 years to get their money. Instead, they might offer you a 30-year amortization (low monthly payments) but require a “balloon” after 5 or 10 years.
This means that at the end of those 5 years, you have to pay off the remaining loan balance in one lump sum. Usually, buyers do this by refinancing into a traditional bank loan once their credit improves or the home’s value increases.
A Real-World Example
Let’s say you want to buy a home for $300,000.
- You offer a 15% down payment ($45,000).
- The seller agrees to finance the remaining $255,000 at a 9% interest rate.
- You agree on a 10-year term with a balloon payment at the end.
- Your monthly principal and interest payment would be $2,050.
This allows you to move in immediately without ever stepping foot inside a bank.
Benefits of In-House Financing for No-Bank Home Buying

Why would someone choose this path? For many, it’s not just a “Plan B”—it’s a strategic move. Here is why in-house financing for real estate is exploding in popularity in 2026.
Speed and Simplicity
Traditional mortgages are a nightmare of paperwork. You have to provide years of tax returns, pay stubs, and explanations for every $50 deposit in your bank account. In-house financing skips the bureaucracy. You can close the deal in a week or two, rather than two months.
Credit Flexibility
This is the biggest draw for no-bank home buying. If you’ve had a past bankruptcy, a foreclosure, or you haven’t built a credit history yet, a bank will see you as a “risk.” A seller, however, sees you as a person. If you can prove you have a steady income and a decent down payment, they are often happy to work with you.
Lower Closing Costs
When you get a bank loan, you are hit with “junk fees”—loan origination fees, processing fees, underwriting fees, and expensive private mortgage insurance (PMI). In a seller-financed deal, many of these costs don’t exist. You save thousands of dollars right at the start.
Customizable Terms
Banks have rigid programs. With in-house financing, you can get creative. You may want to pay a little more each month in exchange for a lower down payment. Or you may want to skip the January payment every year because your business is seasonal. If the seller agrees, it’s a deal!
Building Equity Faster
In a rising market, waiting two years to “fix your credit” could mean the house you want costs $50,000 more by the time you’re ready. By using in-house financing now, you start building equity today. You own the home, and any increase in value belongs to you, not the bank.
Drawbacks and Risks of In-House Financing Real Estate
I want to be completely honest with you: no-bank home buying isn’t all sunshine and rainbows. There are real risks involved that you need to consider before signing on the dotted line.
Higher Interest Rates
Because the seller is taking a bigger risk by not requiring a high credit score, they will charge you for it. Expect to pay 2% to 5% more in interest than you would at a bank. Over time, this adds up to a lot of money.
The Risk of Seller Default
What if the seller still has a mortgage on the house? If you pay the seller, but the seller stops paying their bank, the bank could still foreclose on the house. This is why it is vital to use a third-party escrow company to handle the payments and ensure the underlying mortgage is being paid.
Less Legal Protection
Federal laws heavily regulate banks. Private sellers are not. While there are still laws governing these deals (like the Dodd-Frank Act), you have fewer safety nets if things go wrong.
The Balloon Payment Pressure
If you have a 5-year balloon payment and you can’t get a bank loan when that time is up, you could lose the house and all the money you’ve put into it. You must have a solid “exit strategy” for paying off that final balance.
Who Qualifies for In-House Financing Real Estate?
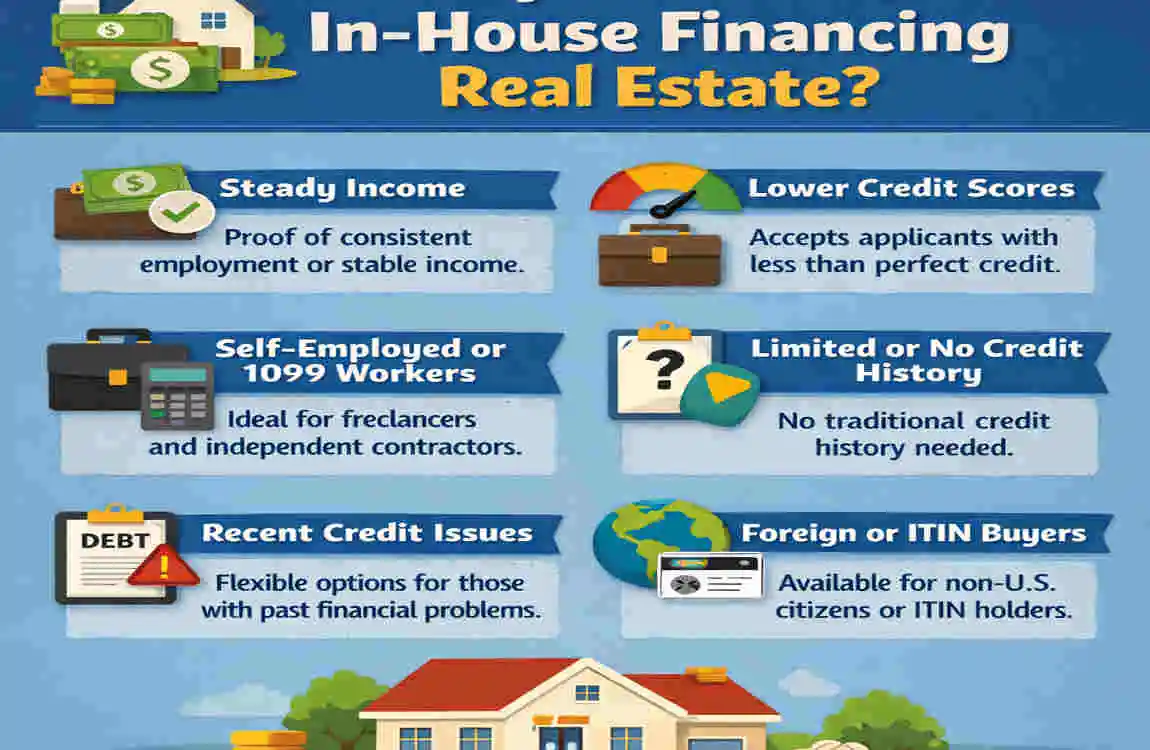
You might be surprised to learn that you don’t need to be “rich” to qualify for in-house financing. However, you do need to prove you are a reliable buyer.
Ideal Candidates for No-Bank Home Buying
- The Self-Employed: If you are a freelancer, business owner, or “gig worker,” your tax returns might show a low net income due to deductions. Sellers care more about your cash flow than your tax returns.
- Real Estate Investors: Investors often use in-house financing to buy properties quickly without hitting the “limit” of how many loans a bank will give them.
- Foreign Nationals: If you are new to the country and don’t yet have a U.S. credit score, in-house financing is one of the few ways to buy a home.
- Credit Builders: People who have the income to support a mortgage but need time to clean up a past credit mistake.
What You Will Need
To secure an in-house financing real estate deal, have these ready:
- Proof of Income: Bank statements from the last 6-12 months.
- A Solid Down Payment: Usually 10% to 20% of the purchase price.
- A Clean Background Check: Most sellers will want to make sure you don’t have a history of evictions.
- A Professional Attitude: Since this is a person-to-person deal, your reputation and how you present yourself matter.
In-House Financing Real Estate vs. Other Options
Is in-house financing the only way to buy without a traditional bank? Not exactly. Let’s see how it stacks up against other popular methods.
Comparison Table: Finding Your Best Path
Option Best For Pros Cons
In-House Financing Bad credit / Fast close Fast, flexible, no bank fees Higher rates, balloon risk
Traditional Mortgage High credit scores Lowest interest rates Strict, slow, high fees
Rent-to-Own Testing a house Low entry cost Don’t own the title yet
Hard Money Loans House flippers High-speed Very high rates (12%+), short terms
Why Choose In-House Over Rent-to-Own?
In a rent-to-own scenario, you are still a tenant. If you miss a payment, you can be evicted like any other renter. In in-house financing, you are the owner. You have the title to the property. This gives you more security and more rights under the law.
How to Find In-House Financing Real Estate Deals

Now for the big question: Where are these magical houses? You won’t usually find them by walking into a big real estate office. You have to be a detective.
Use Specific MLS Keywords
When searching on sites like Zillow or Realtor.com, use the “Keyword” filter. Search for terms like:
- “Owner will finance”
- “Seller carry”
- “Land contract”
- “In-house financing”
Check “For Sale By Owner” (FSBO) Sites
Websites like ForSaleByOwner.com, Facebook Marketplace, and Craigslist are gold mines for these deals. Since these sellers are already avoiding real estate agents, they are often more open to avoiding banks as well.
Talk to Local Real Estate Investors
Join local real estate groups on Facebook. Investors often buy houses, fix them up, and then offer them with in-house financing to get a higher price and a steady stream of interest income.
Drive for Dollars
Sometimes, the best way is the old-fashioned way. Look for handwritten “For Sale” signs in yards. These are usually individual owners who are much more likely to negotiate a private financing deal with you.
Legal and Tax Considerations in In-House Real Estate Financing
Before you hand over your down payment, you need to protect your “legal neck.” This isn’t just a simple purchase; it’s a long-term financial contract.
The Importance of a Title Search
Never buy a house via in-house financing without a professional title search. You need to make sure the seller actually owns the house and that there aren’t any hidden liens (like unpaid property taxes or contractor debts) that will become your problem once you buy it.
Tax Benefits for You
The good news? The IRS generally treats in-house financing the same as a regular mortgage. This means you can deduct the mortgage interest you pay to the seller on your tax return, which saves you a significant amount of money every year.
The Dodd-Frank Act
There are federal laws (like the Dodd-Frank Act) that limit how many houses a private seller can finance each year without being a “licensed lender.” Make sure your seller is following these rules so your contract remains valid and enforceable.
Real-Life Success Stories: No-Bank Home Buying Wins
The Self-Employed Designer
Sarah was a successful freelance graphic designer making $120,000 a year. However, because she had many business write-offs, her “taxable income” appeared too low for a bank. She found a retired couple selling their home who agreed to in-house financing. Sarah put 20% down, and three years later, she had enough “official” income history to refinance into a lower-rate bank loan.
The Credit Rebuilder
Marcus had a medical emergency that tanked his credit score to 540. He couldn’t get a bank to look at him. He found a developer offering builder in-house financing on a new townhome. By paying a slightly higher interest rate for four years, Marcus was able to own his home while his credit score naturally recovered. Today, he has over $80,000 in equity.
FAQs About In-House Financing Real Estate
What is in-house financing real estate exactly?
It is a property purchase where the seller or builder provides the loan directly to the buyer, bypassing traditional banks and mortgage companies.
Is in-house financing legit for buying homes?
Yes, it is an entirely legal and common practice. However, it must be documented correctly with a promissory note and a deed of trust to protect both parties.
Do I still need a down payment for no-bank home buying?
Usually, yes. In fact, sellers often require a larger down payment (10-20%) to offset the risk of not checking your credit as strictly as a bank would.
Can I refinance an in-house financing loan?
Absolutely. Most people use in-house financing as a “bridge.” Once their credit improves or the home value increases, they refinance into a traditional bank mortgage with a lower interest rate.
What happens if I miss a payment?
Just like a bank mortgage, if you stop paying, the seller has the right to foreclose on the property and take it back. Always make sure your payments are recorded and sent through a third-party service.
Are interest rates higher with in-house financing?
Typically, yes. Because the seller is taking on more risk, they usually charge 2% to 5% above the current market rate for traditional mortgages.